Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
/**
* Base BigInteger Engine
*
* PHP version 5 and 7
*
* @author Jim Wigginton <terrafrost@php.net>
* @copyright 2017 Jim Wigginton
* @license http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html MIT License
* @link http://pear.php.net/package/Math_BigInteger
*/
namespace phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger\Engines;
use phpseclib3\Common\Functions\Strings;
use phpseclib3\Crypt\Random;
use phpseclib3\Exception\BadConfigurationException;
use phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger;
/**
* Base Engine.
*
* @author Jim Wigginton <terrafrost@php.net>
*/
abstract class Engine implements \JsonSerializable
{
/* final protected */ const PRIMES = [
3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59,
61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137,
139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227,
229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293, 307, 311, 313,
317, 331, 337, 347, 349, 353, 359, 367, 373, 379, 383, 389, 397, 401, 409, 419,
421, 431, 433, 439, 443, 449, 457, 461, 463, 467, 479, 487, 491, 499, 503, 509,
521, 523, 541, 547, 557, 563, 569, 571, 577, 587, 593, 599, 601, 607, 613, 617,
619, 631, 641, 643, 647, 653, 659, 661, 673, 677, 683, 691, 701, 709, 719, 727,
733, 739, 743, 751, 757, 761, 769, 773, 787, 797, 809, 811, 821, 823, 827, 829,
839, 853, 857, 859, 863, 877, 881, 883, 887, 907, 911, 919, 929, 937, 941, 947,
953, 967, 971, 977, 983, 991, 997,
];
/**
* BigInteger(0)
*
* @var array<class-string<static>, static>
*/
protected static $zero = [];
/**
* BigInteger(1)
*
* @var array<class-string<static>, static>
*/
protected static $one = [];
/**
* BigInteger(2)
*
* @var array<class-string<static>, static>
*/
protected static $two = [];
/**
* Modular Exponentiation Engine
*
* @var array<class-string<static>, class-string<static>>
*/
protected static $modexpEngine;
/**
* Engine Validity Flag
*
* @var array<class-string<static>, bool>
*/
protected static $isValidEngine;
/**
* Holds the BigInteger's value
*
* @var \GMP|string|array|int
*/
protected $value;
/**
* Holds the BigInteger's sign
*
* @var bool
*/
protected $is_negative;
/**
* Precision
*
* @see static::setPrecision()
* @var int
*/
protected $precision = -1;
/**
* Precision Bitmask
*
* @see static::setPrecision()
* @var static|false
*/
protected $bitmask = false;
/**
* Recurring Modulo Function
*
* @var callable
*/
protected $reduce;
/**
* Mode independent value used for serialization.
*
* @see self::__sleep()
* @see self::__wakeup()
* @var string
*/
protected $hex;
/**
* Default constructor
*
* @param int|numeric-string $x integer Base-10 number or base-$base number if $base set.
* @param int $base
*/
public function __construct($x = 0, $base = 10)
{
if (!array_key_exists(static::class, static::$zero)) {
static::$zero[static::class] = null; // Placeholder to prevent infinite loop.
static::$zero[static::class] = new static(0);
static::$one[static::class] = new static(1);
static::$two[static::class] = new static(2);
}
// '0' counts as empty() but when the base is 256 '0' is equal to ord('0') or 48
// '0' is the only value like this per http://php.net/empty
if (empty($x) && (abs($base) != 256 || $x !== '0')) {
return;
}
switch ($base) {
case -256:
case 256:
if ($base == -256 && (ord($x[0]) & 0x80)) {
$this->value = ~$x;
$this->is_negative = true;
} else {
$this->value = $x;
$this->is_negative = false;
}
$this->initialize($base);
if ($this->is_negative) {
$temp = $this->add(new static('-1'));
$this->value = $temp->value;
}
break;
case -16:
case 16:
if ($base > 0 && $x[0] == '-') {
$this->is_negative = true;
$x = substr($x, 1);
}
$x = preg_replace('#^(?:0x)?([A-Fa-f0-9]*).*#s', '$1', $x);
$is_negative = false;
if ($base < 0 && hexdec($x[0]) >= 8) {
$this->is_negative = $is_negative = true;
$x = Strings::bin2hex(~Strings::hex2bin($x));
}
$this->value = $x;
$this->initialize($base);
if ($is_negative) {
$temp = $this->add(new static('-1'));
$this->value = $temp->value;
}
break;
case -10:
case 10:
// (?<!^)(?:-).*: find any -'s that aren't at the beginning and then any characters that follow that
// (?<=^|-)0*: find any 0's that are preceded by the start of the string or by a - (ie. octals)
// [^-0-9].*: find any non-numeric characters and then any characters that follow that
$this->value = preg_replace('#(?<!^)(?:-).*|(?<=^|-)0*|[^-0-9].*#s', '', $x);
if (!strlen($this->value) || $this->value == '-') {
$this->value = '0';
}
$this->initialize($base);
break;
case -2:
case 2:
if ($base > 0 && $x[0] == '-') {
$this->is_negative = true;
$x = substr($x, 1);
}
$x = preg_replace('#^([01]*).*#s', '$1', $x);
$temp = new static(Strings::bits2bin($x), 128 * $base); // ie. either -16 or +16
$this->value = $temp->value;
if ($temp->is_negative) {
$this->is_negative = true;
}
break;
default:
// base not supported, so we'll let $this == 0
}
}
/**
* Sets engine type.
*
* Throws an exception if the type is invalid
*
* @param class-string<Engine> $engine
*/
public static function setModExpEngine($engine)
{
$fqengine = '\\phpseclib3\\Math\\BigInteger\\Engines\\' . static::ENGINE_DIR . '\\' . $engine;
if (!class_exists($fqengine) || !method_exists($fqengine, 'isValidEngine')) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException("$engine is not a valid engine");
}
if (!$fqengine::isValidEngine()) {
throw new BadConfigurationException("$engine is not setup correctly on this system");
}
static::$modexpEngine[static::class] = $fqengine;
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a byte string (eg. base-256).
*
* Negative numbers are saved as positive numbers, unless $twos_compliment is set to true, at which point, they're
* saved as two's compliment.
* @return string
*/
protected function toBytesHelper()
{
$comparison = $this->compare(new static());
if ($comparison == 0) {
return $this->precision > 0 ? str_repeat(chr(0), ($this->precision + 1) >> 3) : '';
}
$temp = $comparison < 0 ? $this->add(new static(1)) : $this;
$bytes = $temp->toBytes();
if (!strlen($bytes)) { // eg. if the number we're trying to convert is -1
$bytes = chr(0);
}
if (ord($bytes[0]) & 0x80) {
$bytes = chr(0) . $bytes;
}
return $comparison < 0 ? ~$bytes : $bytes;
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a hex string (eg. base-16).
*
* @param bool $twos_compliment
* @return string
*/
public function toHex($twos_compliment = false)
{
return Strings::bin2hex($this->toBytes($twos_compliment));
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a bit string (eg. base-2).
*
* Negative numbers are saved as positive numbers, unless $twos_compliment is set to true, at which point, they're
* saved as two's compliment.
*
* @param bool $twos_compliment
* @return string
*/
public function toBits($twos_compliment = false)
{
$hex = $this->toBytes($twos_compliment);
$bits = Strings::bin2bits($hex);
$result = $this->precision > 0 ? substr($bits, -$this->precision) : ltrim($bits, '0');
if ($twos_compliment && $this->compare(new static()) > 0 && $this->precision <= 0) {
return '0' . $result;
}
return $result;
}
/**
* Calculates modular inverses.
*
* Say you have (30 mod 17 * x mod 17) mod 17 == 1. x can be found using modular inverses.
*
* {@internal See {@link http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac/about/chap14.pdf#page=21 HAC 14.64} for more information.}
*
* @param Engine $n
* @return static|false
*/
protected function modInverseHelper(Engine $n)
{
// $x mod -$n == $x mod $n.
$n = $n->abs();
if ($this->compare(static::$zero[static::class]) < 0) {
$temp = $this->abs();
$temp = $temp->modInverse($n);
return $this->normalize($n->subtract($temp));
}
extract($this->extendedGCD($n));
/**
* @var Engine $gcd
* @var Engine $x
*/
if (!$gcd->equals(static::$one[static::class])) {
return false;
}
$x = $x->compare(static::$zero[static::class]) < 0 ? $x->add($n) : $x;
return $this->compare(static::$zero[static::class]) < 0 ? $this->normalize($n->subtract($x)) : $this->normalize($x);
}
/**
* Serialize
*
* Will be called, automatically, when serialize() is called on a BigInteger object.
*
* @return array
*/
public function __sleep()
{
$this->hex = $this->toHex(true);
$vars = ['hex'];
if ($this->precision > 0) {
$vars[] = 'precision';
}
return $vars;
}
/**
* Serialize
*
* Will be called, automatically, when unserialize() is called on a BigInteger object.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __wakeup()
{
$temp = new static($this->hex, -16);
$this->value = $temp->value;
$this->is_negative = $temp->is_negative;
if ($this->precision > 0) {
// recalculate $this->bitmask
$this->setPrecision($this->precision);
}
}
/**
* JSON Serialize
*
* Will be called, automatically, when json_encode() is called on a BigInteger object.
*
* @return array{hex: string, precision?: int]
*/
#[\ReturnTypeWillChange]
public function jsonSerialize()
{
$result = ['hex' => $this->toHex(true)];
if ($this->precision > 0) {
$result['precision'] = $this->precision;
}
return $result;
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a base-10 number.
*
* @return string
*/
public function __toString()
{
return $this->toString();
}
/**
* __debugInfo() magic method
*
* Will be called, automatically, when print_r() or var_dump() are called
*
* @return array
*/
public function __debugInfo()
{
$result = [
'value' => '0x' . $this->toHex(true),
'engine' => basename(static::class)
];
return $this->precision > 0 ? $result + ['precision' => $this->precision] : $result;
}
/**
* Set Precision
*
* Some bitwise operations give different results depending on the precision being used. Examples include left
* shift, not, and rotates.
*
* @param int $bits
*/
public function setPrecision($bits)
{
if ($bits < 1) {
$this->precision = -1;
$this->bitmask = false;
return;
}
$this->precision = $bits;
$this->bitmask = static::setBitmask($bits);
$temp = $this->normalize($this);
$this->value = $temp->value;
}
/**
* Get Precision
*
* Returns the precision if it exists, -1 if it doesn't
*
* @return int
*/
public function getPrecision()
{
return $this->precision;
}
/**
* Set Bitmask
* @return static
* @param int $bits
* @see self::setPrecision()
*/
protected static function setBitmask($bits)
{
return new static(chr((1 << ($bits & 0x7)) - 1) . str_repeat(chr(0xFF), $bits >> 3), 256);
}
/**
* Logical Not
*
* @return Engine|string
*/
public function bitwise_not()
{
// calculuate "not" without regard to $this->precision
// (will always result in a smaller number. ie. ~1 isn't 1111 1110 - it's 0)
$temp = $this->toBytes();
if ($temp == '') {
return $this->normalize(static::$zero[static::class]);
}
$pre_msb = decbin(ord($temp[0]));
$temp = ~$temp;
$msb = decbin(ord($temp[0]));
if (strlen($msb) == 8) {
$msb = substr($msb, strpos($msb, '0'));
}
$temp[0] = chr(bindec($msb));
// see if we need to add extra leading 1's
$current_bits = strlen($pre_msb) + 8 * strlen($temp) - 8;
$new_bits = $this->precision - $current_bits;
if ($new_bits <= 0) {
return $this->normalize(new static($temp, 256));
}
// generate as many leading 1's as we need to.
$leading_ones = chr((1 << ($new_bits & 0x7)) - 1) . str_repeat(chr(0xFF), $new_bits >> 3);
self::base256_lshift($leading_ones, $current_bits);
$temp = str_pad($temp, strlen($leading_ones), chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
return $this->normalize(new static($leading_ones | $temp, 256));
}
/**
* Logical Left Shift
*
* Shifts binary strings $shift bits, essentially multiplying by 2**$shift.
*
* @param string $x
* @param int $shift
* @return void
*/
protected static function base256_lshift(&$x, $shift)
{
if ($shift == 0) {
return;
}
$num_bytes = $shift >> 3; // eg. floor($shift/8)
$shift &= 7; // eg. $shift % 8
$carry = 0;
for ($i = strlen($x) - 1; $i >= 0; --$i) {
$temp = ord($x[$i]) << $shift | $carry;
$x[$i] = chr($temp);
$carry = $temp >> 8;
}
$carry = ($carry != 0) ? chr($carry) : '';
$x = $carry . $x . str_repeat(chr(0), $num_bytes);
}
/**
* Logical Left Rotate
*
* Instead of the top x bits being dropped they're appended to the shifted bit string.
*
* @param int $shift
* @return Engine
*/
public function bitwise_leftRotate($shift)
{
$bits = $this->toBytes();
if ($this->precision > 0) {
$precision = $this->precision;
if (static::FAST_BITWISE) {
$mask = $this->bitmask->toBytes();
} else {
$mask = $this->bitmask->subtract(new static(1));
$mask = $mask->toBytes();
}
} else {
$temp = ord($bits[0]);
for ($i = 0; $temp >> $i; ++$i) {
}
$precision = 8 * strlen($bits) - 8 + $i;
$mask = chr((1 << ($precision & 0x7)) - 1) . str_repeat(chr(0xFF), $precision >> 3);
}
if ($shift < 0) {
$shift += $precision;
}
$shift %= $precision;
if (!$shift) {
return clone $this;
}
$left = $this->bitwise_leftShift($shift);
$left = $left->bitwise_and(new static($mask, 256));
$right = $this->bitwise_rightShift($precision - $shift);
$result = static::FAST_BITWISE ? $left->bitwise_or($right) : $left->add($right);
return $this->normalize($result);
}
/**
* Logical Right Rotate
*
* Instead of the bottom x bits being dropped they're prepended to the shifted bit string.
*
* @param int $shift
* @return Engine
*/
public function bitwise_rightRotate($shift)
{
return $this->bitwise_leftRotate(-$shift);
}
/**
* Returns the smallest and largest n-bit number
*
* @param int $bits
* @return array{min: static, max: static}
*/
public static function minMaxBits($bits)
{
$bytes = $bits >> 3;
$min = str_repeat(chr(0), $bytes);
$max = str_repeat(chr(0xFF), $bytes);
$msb = $bits & 7;
if ($msb) {
$min = chr(1 << ($msb - 1)) . $min;
$max = chr((1 << $msb) - 1) . $max;
} else {
$min[0] = chr(0x80);
}
return [
'min' => new static($min, 256),
'max' => new static($max, 256)
];
}
/**
* Return the size of a BigInteger in bits
*
* @return int
*/
public function getLength()
{
return strlen($this->toBits());
}
/**
* Return the size of a BigInteger in bytes
*
* @return int
*/
public function getLengthInBytes()
{
return (int) ceil($this->getLength() / 8);
}
/**
* Performs some pre-processing for powMod
*
* @param Engine $e
* @param Engine $n
* @return static|false
*/
protected function powModOuter(Engine $e, Engine $n)
{
$n = $this->bitmask !== false && $this->bitmask->compare($n) < 0 ? $this->bitmask : $n->abs();
if ($e->compare(new static()) < 0) {
$e = $e->abs();
$temp = $this->modInverse($n);
if ($temp === false) {
return false;
}
return $this->normalize($temp->powModInner($e, $n));
}
if ($this->compare($n) > 0) {
list(, $temp) = $this->divide($n);
return $temp->powModInner($e, $n);
}
return $this->powModInner($e, $n);
}
/**
* Sliding Window k-ary Modular Exponentiation
*
* Based on {@link http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac/about/chap14.pdf#page=27 HAC 14.85} /
* {@link http://math.libtomcrypt.com/files/tommath.pdf#page=210 MPM 7.7}. In a departure from those algorithims,
* however, this function performs a modular reduction after every multiplication and squaring operation.
* As such, this function has the same preconditions that the reductions being used do.
*
* @template T of Engine
* @param Engine $x
* @param Engine $e
* @param Engine $n
* @param class-string<T> $class
* @return T
*/
protected static function slidingWindow(Engine $x, Engine $e, Engine $n, $class)
{
static $window_ranges = [7, 25, 81, 241, 673, 1793]; // from BigInteger.java's oddModPow function
//static $window_ranges = [0, 7, 36, 140, 450, 1303, 3529]; // from MPM 7.3.1
$e_bits = $e->toBits();
$e_length = strlen($e_bits);
// calculate the appropriate window size.
// $window_size == 3 if $window_ranges is between 25 and 81, for example.
for ($i = 0, $window_size = 1; $i < count($window_ranges) && $e_length > $window_ranges[$i]; ++$window_size, ++$i) {
}
$n_value = $n->value;
if (method_exists(static::class, 'generateCustomReduction')) {
static::generateCustomReduction($n, $class);
}
// precompute $this^0 through $this^$window_size
$powers = [];
$powers[1] = static::prepareReduce($x->value, $n_value, $class);
$powers[2] = static::squareReduce($powers[1], $n_value, $class);
// we do every other number since substr($e_bits, $i, $j+1) (see below) is supposed to end
// in a 1. ie. it's supposed to be odd.
$temp = 1 << ($window_size - 1);
for ($i = 1; $i < $temp; ++$i) {
$i2 = $i << 1;
$powers[$i2 + 1] = static::multiplyReduce($powers[$i2 - 1], $powers[2], $n_value, $class);
}
$result = new $class(1);
$result = static::prepareReduce($result->value, $n_value, $class);
for ($i = 0; $i < $e_length;) {
if (!$e_bits[$i]) {
$result = static::squareReduce($result, $n_value, $class);
++$i;
} else {
for ($j = $window_size - 1; $j > 0; --$j) {
if (!empty($e_bits[$i + $j])) {
break;
}
}
// eg. the length of substr($e_bits, $i, $j + 1)
for ($k = 0; $k <= $j; ++$k) {
$result = static::squareReduce($result, $n_value, $class);
}
$result = static::multiplyReduce($result, $powers[bindec(substr($e_bits, $i, $j + 1))], $n_value, $class);
$i += $j + 1;
}
}
$temp = new $class();
$temp->value = static::reduce($result, $n_value, $class);
return $temp;
}
/**
* Generates a random number of a certain size
*
* Bit length is equal to $size
*
* @param int $size
* @return Engine
*/
public static function random($size)
{
extract(static::minMaxBits($size));
/**
* @var BigInteger $min
* @var BigInteger $max
*/
return static::randomRange($min, $max);
}
/**
* Generates a random prime number of a certain size
*
* Bit length is equal to $size
*
* @param int $size
* @return Engine
*/
public static function randomPrime($size)
{
extract(static::minMaxBits($size));
/**
* @var static $min
* @var static $max
*/
return static::randomRangePrime($min, $max);
}
/**
* Performs some pre-processing for randomRangePrime
*
* @param Engine $min
* @param Engine $max
* @return static|false
*/
protected static function randomRangePrimeOuter(Engine $min, Engine $max)
{
$compare = $max->compare($min);
if (!$compare) {
return $min->isPrime() ? $min : false;
} elseif ($compare < 0) {
// if $min is bigger then $max, swap $min and $max
$temp = $max;
$max = $min;
$min = $temp;
}
$length = $max->getLength();
if ($length > 8196) {
throw new \RuntimeException("Generation of random prime numbers larger than 8196 has been disabled ($length)");
}
$x = static::randomRange($min, $max);
return static::randomRangePrimeInner($x, $min, $max);
}
/**
* Generate a random number between a range
*
* Returns a random number between $min and $max where $min and $max
* can be defined using one of the two methods:
*
* BigInteger::randomRange($min, $max)
* BigInteger::randomRange($max, $min)
*
* @param Engine $min
* @param Engine $max
* @return Engine
*/
protected static function randomRangeHelper(Engine $min, Engine $max)
{
$compare = $max->compare($min);
if (!$compare) {
return $min;
} elseif ($compare < 0) {
// if $min is bigger then $max, swap $min and $max
$temp = $max;
$max = $min;
$min = $temp;
}
if (!isset(static::$one[static::class])) {
static::$one[static::class] = new static(1);
}
$max = $max->subtract($min->subtract(static::$one[static::class]));
$size = strlen(ltrim($max->toBytes(), chr(0)));
/*
doing $random % $max doesn't work because some numbers will be more likely to occur than others.
eg. if $max is 140 and $random's max is 255 then that'd mean both $random = 5 and $random = 145
would produce 5 whereas the only value of random that could produce 139 would be 139. ie.
not all numbers would be equally likely. some would be more likely than others.
creating a whole new random number until you find one that is within the range doesn't work
because, for sufficiently small ranges, the likelihood that you'd get a number within that range
would be pretty small. eg. with $random's max being 255 and if your $max being 1 the probability
would be pretty high that $random would be greater than $max.
phpseclib works around this using the technique described here:
http://crypto.stackexchange.com/questions/5708/creating-a-small-number-from-a-cryptographically-secure-random-string
*/
$random_max = new static(chr(1) . str_repeat("\0", $size), 256);
$random = new static(Random::string($size), 256);
list($max_multiple) = $random_max->divide($max);
$max_multiple = $max_multiple->multiply($max);
while ($random->compare($max_multiple) >= 0) {
$random = $random->subtract($max_multiple);
$random_max = $random_max->subtract($max_multiple);
$random = $random->bitwise_leftShift(8);
$random = $random->add(new static(Random::string(1), 256));
$random_max = $random_max->bitwise_leftShift(8);
list($max_multiple) = $random_max->divide($max);
$max_multiple = $max_multiple->multiply($max);
}
list(, $random) = $random->divide($max);
return $random->add($min);
}
/**
* Performs some post-processing for randomRangePrime
*
* @param Engine $x
* @param Engine $min
* @param Engine $max
* @return static|false
*/
protected static function randomRangePrimeInner(Engine $x, Engine $min, Engine $max)
{
if (!isset(static::$two[static::class])) {
static::$two[static::class] = new static('2');
}
$x->make_odd();
if ($x->compare($max) > 0) {
// if $x > $max then $max is even and if $min == $max then no prime number exists between the specified range
if ($min->equals($max)) {
return false;
}
$x = clone $min;
$x->make_odd();
}
$initial_x = clone $x;
while (true) {
if ($x->isPrime()) {
return $x;
}
$x = $x->add(static::$two[static::class]);
if ($x->compare($max) > 0) {
$x = clone $min;
if ($x->equals(static::$two[static::class])) {
return $x;
}
$x->make_odd();
}
if ($x->equals($initial_x)) {
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* Sets the $t parameter for primality testing
*
* @return int
*/
protected function setupIsPrime()
{
$length = $this->getLengthInBytes();
// see HAC 4.49 "Note (controlling the error probability)"
// @codingStandardsIgnoreStart
if ($length >= 163) { $t = 2; } // floor(1300 / 8)
else if ($length >= 106) { $t = 3; } // floor( 850 / 8)
else if ($length >= 81 ) { $t = 4; } // floor( 650 / 8)
else if ($length >= 68 ) { $t = 5; } // floor( 550 / 8)
else if ($length >= 56 ) { $t = 6; } // floor( 450 / 8)
else if ($length >= 50 ) { $t = 7; } // floor( 400 / 8)
else if ($length >= 43 ) { $t = 8; } // floor( 350 / 8)
else if ($length >= 37 ) { $t = 9; } // floor( 300 / 8)
else if ($length >= 31 ) { $t = 12; } // floor( 250 / 8)
else if ($length >= 25 ) { $t = 15; } // floor( 200 / 8)
else if ($length >= 18 ) { $t = 18; } // floor( 150 / 8)
else { $t = 27; }
// @codingStandardsIgnoreEnd
return $t;
}
/**
* Tests Primality
*
* Uses the {@link http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miller%E2%80%93Rabin_primality_test Miller-Rabin primality test}.
* See {@link http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac/about/chap4.pdf#page=8 HAC 4.24} for more info.
*
* @param int $t
* @return bool
*/
protected function testPrimality($t)
{
if (!$this->testSmallPrimes()) {
return false;
}
$n = clone $this;
$n_1 = $n->subtract(static::$one[static::class]);
$n_2 = $n->subtract(static::$two[static::class]);
$r = clone $n_1;
$s = static::scan1divide($r);
for ($i = 0; $i < $t; ++$i) {
$a = static::randomRange(static::$two[static::class], $n_2);
$y = $a->modPow($r, $n);
if (!$y->equals(static::$one[static::class]) && !$y->equals($n_1)) {
for ($j = 1; $j < $s && !$y->equals($n_1); ++$j) {
$y = $y->modPow(static::$two[static::class], $n);
if ($y->equals(static::$one[static::class])) {
return false;
}
}
if (!$y->equals($n_1)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Checks a numer to see if it's prime
*
* Assuming the $t parameter is not set, this function has an error rate of 2**-80. The main motivation for the
* $t parameter is distributability. BigInteger::randomPrime() can be distributed across multiple pageloads
* on a website instead of just one.
*
* @param int|bool $t
* @return bool
*/
public function isPrime($t = false)
{
// OpenSSL limits RSA keys to 16384 bits. The length of an RSA key is equal to the length of the modulo, which is
// produced by multiplying the primes p and q by one another. The largest number two 8196 bit primes can produce is
// a 16384 bit number so, basically, 8196 bit primes are the largest OpenSSL will generate and if that's the largest
// that it'll generate it also stands to reason that that's the largest you'll be able to test primality on
$length = $this->getLength();
if ($length > 8196) {
throw new \RuntimeException("Primality testing is not supported for numbers larger than 8196 bits ($length)");
}
if (!$t) {
$t = $this->setupIsPrime();
}
return $this->testPrimality($t);
}
/**
* Performs a few preliminary checks on root
*
* @param int $n
* @return Engine
*/
protected function rootHelper($n)
{
if ($n < 1) {
return clone static::$zero[static::class];
} // we want positive exponents
if ($this->compare(static::$one[static::class]) < 0) {
return clone static::$zero[static::class];
} // we want positive numbers
if ($this->compare(static::$two[static::class]) < 0) {
return clone static::$one[static::class];
} // n-th root of 1 or 2 is 1
return $this->rootInner($n);
}
/**
* Calculates the nth root of a biginteger.
*
* Returns the nth root of a positive biginteger, where n defaults to 2
*
* {@internal This function is based off of {@link http://mathforum.org/library/drmath/view/52605.html this page} and {@link http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11242920/calculating-nth-root-with-bcmath-in-php this stackoverflow question}.}
*
* @param int $n
* @return Engine
*/
protected function rootInner($n)
{
$n = new static($n);
// g is our guess number
$g = static::$two[static::class];
// while (g^n < num) g=g*2
while ($g->pow($n)->compare($this) < 0) {
$g = $g->multiply(static::$two[static::class]);
}
// if (g^n==num) num is a power of 2, we're lucky, end of job
// == 0 bccomp(bcpow($g, $n), $n->value)==0
if ($g->pow($n)->equals($this) > 0) {
$root = $g;
return $this->normalize($root);
}
// if we're here num wasn't a power of 2 :(
$og = $g; // og means original guess and here is our upper bound
$g = $g->divide(static::$two[static::class])[0]; // g is set to be our lower bound
$step = $og->subtract($g)->divide(static::$two[static::class])[0]; // step is the half of upper bound - lower bound
$g = $g->add($step); // we start at lower bound + step , basically in the middle of our interval
// while step>1
while ($step->compare(static::$one[static::class]) == 1) {
$guess = $g->pow($n);
$step = $step->divide(static::$two[static::class])[0];
$comp = $guess->compare($this); // compare our guess with real number
switch ($comp) {
case -1: // if guess is lower we add the new step
$g = $g->add($step);
break;
case 1: // if guess is higher we sub the new step
$g = $g->subtract($step);
break;
case 0: // if guess is exactly the num we're done, we return the value
$root = $g;
break 2;
}
}
if ($comp == 1) {
$g = $g->subtract($step);
}
// whatever happened, g is the closest guess we can make so return it
$root = $g;
return $this->normalize($root);
}
/**
* Calculates the nth root of a biginteger.
*
* @param int $n
* @return Engine
*/
public function root($n = 2)
{
return $this->rootHelper($n);
}
/**
* Return the minimum BigInteger between an arbitrary number of BigIntegers.
*
* @param array $nums
* @return Engine
*/
protected static function minHelper(array $nums)
{
if (count($nums) == 1) {
return $nums[0];
}
$min = $nums[0];
for ($i = 1; $i < count($nums); $i++) {
$min = $min->compare($nums[$i]) > 0 ? $nums[$i] : $min;
}
return $min;
}
/**
* Return the minimum BigInteger between an arbitrary number of BigIntegers.
*
* @param array $nums
* @return Engine
*/
protected static function maxHelper(array $nums)
{
if (count($nums) == 1) {
return $nums[0];
}
$max = $nums[0];
for ($i = 1; $i < count($nums); $i++) {
$max = $max->compare($nums[$i]) < 0 ? $nums[$i] : $max;
}
return $max;
}
/**
* Create Recurring Modulo Function
*
* Sometimes it may be desirable to do repeated modulos with the same number outside of
* modular exponentiation
*
* @return callable
*/
public function createRecurringModuloFunction()
{
$class = static::class;
$fqengine = !method_exists(static::$modexpEngine[static::class], 'reduce') ?
'\\phpseclib3\\Math\\BigInteger\\Engines\\' . static::ENGINE_DIR . '\\DefaultEngine' :
static::$modexpEngine[static::class];
if (method_exists($fqengine, 'generateCustomReduction')) {
$func = $fqengine::generateCustomReduction($this, static::class);
return eval('return function(' . static::class . ' $x) use ($func, $class) {
$r = new $class();
$r->value = $func($x->value);
return $r;
};');
}
$n = $this->value;
return eval('return function(' . static::class . ' $x) use ($n, $fqengine, $class) {
$r = new $class();
$r->value = $fqengine::reduce($x->value, $n, $class);
return $r;
};');
}
/**
* Calculates the greatest common divisor and Bezout's identity.
*
* @param Engine $n
* @return array{gcd: Engine, x: Engine, y: Engine}
*/
protected function extendedGCDHelper(Engine $n)
{
$u = clone $this;
$v = clone $n;
$one = new static(1);
$zero = new static();
$a = clone $one;
$b = clone $zero;
$c = clone $zero;
$d = clone $one;
while (!$v->equals($zero)) {
list($q) = $u->divide($v);
$temp = $u;
$u = $v;
$v = $temp->subtract($v->multiply($q));
$temp = $a;
$a = $c;
$c = $temp->subtract($a->multiply($q));
$temp = $b;
$b = $d;
$d = $temp->subtract($b->multiply($q));
}
return [
'gcd' => $u,
'x' => $a,
'y' => $b
];
}
/**
* Bitwise Split
*
* Splits BigInteger's into chunks of $split bits
*
* @param int $split
* @return Engine[]
*/
public function bitwise_split($split)
{
if ($split < 1) {
throw new \RuntimeException('Offset must be greater than 1');
}
$mask = static::$one[static::class]->bitwise_leftShift($split)->subtract(static::$one[static::class]);
$num = clone $this;
$vals = [];
while (!$num->equals(static::$zero[static::class])) {
$vals[] = $num->bitwise_and($mask);
$num = $num->bitwise_rightShift($split);
}
return array_reverse($vals);
}
/**
* Logical And
*
* @param Engine $x
* @return Engine
*/
protected function bitwiseAndHelper(Engine $x)
{
$left = $this->toBytes(true);
$right = $x->toBytes(true);
$length = max(strlen($left), strlen($right));
$left = str_pad($left, $length, chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
$right = str_pad($right, $length, chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
return $this->normalize(new static($left & $right, -256));
}
/**
* Logical Or
*
* @param Engine $x
* @return Engine
*/
protected function bitwiseOrHelper(Engine $x)
{
$left = $this->toBytes(true);
$right = $x->toBytes(true);
$length = max(strlen($left), strlen($right));
$left = str_pad($left, $length, chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
$right = str_pad($right, $length, chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
return $this->normalize(new static($left | $right, -256));
}
/**
* Logical Exclusive Or
*
* @param Engine $x
* @return Engine
*/
protected function bitwiseXorHelper(Engine $x)
{
$left = $this->toBytes(true);
$right = $x->toBytes(true);
$length = max(strlen($left), strlen($right));
$left = str_pad($left, $length, chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
$right = str_pad($right, $length, chr(0), STR_PAD_LEFT);
return $this->normalize(new static($left ^ $right, -256));
}
}
How it Works

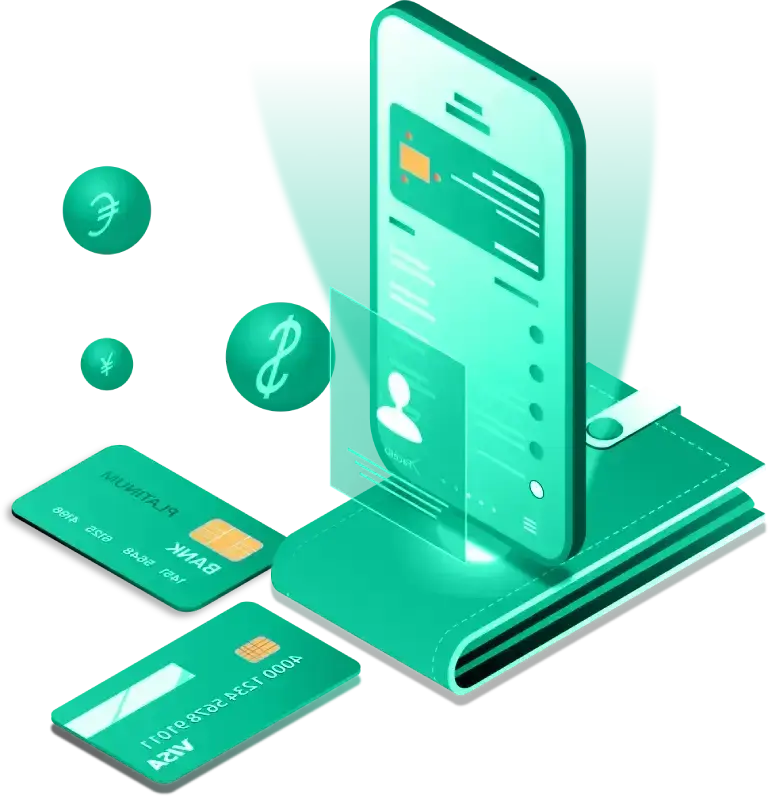
Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
