Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
/*
* This file is part of PHPUnit.
*
* (c) Sebastian Bergmann <sebastian@phpunit.de>
*
* For the full copyright and license information, please view the LICENSE
* file that was distributed with this source code.
*/
namespace PHPUnit\Framework\Constraint;
use function sprintf;
use Countable;
use PHPUnit\Framework\ExpectationFailedException;
use PHPUnit\Framework\SelfDescribing;
use SebastianBergmann\Comparator\ComparisonFailure;
use SebastianBergmann\Exporter\Exporter;
use SebastianBergmann\RecursionContext\InvalidArgumentException;
/**
* @no-named-arguments Parameter names are not covered by the backward compatibility promise for PHPUnit
*/
abstract class Constraint implements Countable, SelfDescribing
{
/**
* @var ?Exporter
*/
private $exporter;
/**
* Evaluates the constraint for parameter $other.
*
* If $returnResult is set to false (the default), an exception is thrown
* in case of a failure. null is returned otherwise.
*
* If $returnResult is true, the result of the evaluation is returned as
* a boolean value instead: true in case of success, false in case of a
* failure.
*
* @throws ExpectationFailedException
* @throws InvalidArgumentException
*/
public function evaluate($other, string $description = '', bool $returnResult = false): ?bool
{
$success = false;
if ($this->matches($other)) {
$success = true;
}
if ($returnResult) {
return $success;
}
if (!$success) {
$this->fail($other, $description);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Counts the number of constraint elements.
*/
public function count(): int
{
return 1;
}
protected function exporter(): Exporter
{
if ($this->exporter === null) {
$this->exporter = new Exporter;
}
return $this->exporter;
}
/**
* Evaluates the constraint for parameter $other. Returns true if the
* constraint is met, false otherwise.
*
* This method can be overridden to implement the evaluation algorithm.
*
* @param mixed $other value or object to evaluate
*
* @codeCoverageIgnore
*/
protected function matches($other): bool
{
return false;
}
/**
* Throws an exception for the given compared value and test description.
*
* @param mixed $other evaluated value or object
* @param string $description Additional information about the test
*
* @throws ExpectationFailedException
* @throws InvalidArgumentException
*
* @psalm-return never-return
*/
protected function fail($other, $description, ?ComparisonFailure $comparisonFailure = null): void
{
$failureDescription = sprintf(
'Failed asserting that %s.',
$this->failureDescription($other),
);
$additionalFailureDescription = $this->additionalFailureDescription($other);
if ($additionalFailureDescription) {
$failureDescription .= "\n" . $additionalFailureDescription;
}
if (!empty($description)) {
$failureDescription = $description . "\n" . $failureDescription;
}
throw new ExpectationFailedException(
$failureDescription,
$comparisonFailure,
);
}
/**
* Return additional failure description where needed.
*
* The function can be overridden to provide additional failure
* information like a diff
*
* @param mixed $other evaluated value or object
*/
protected function additionalFailureDescription($other): string
{
return '';
}
/**
* Returns the description of the failure.
*
* The beginning of failure messages is "Failed asserting that" in most
* cases. This method should return the second part of that sentence.
*
* To provide additional failure information additionalFailureDescription
* can be used.
*
* @param mixed $other evaluated value or object
*
* @throws InvalidArgumentException
*/
protected function failureDescription($other): string
{
return $this->exporter()->export($other) . ' ' . $this->toString();
}
/**
* Returns a custom string representation of the constraint object when it
* appears in context of an $operator expression.
*
* The purpose of this method is to provide meaningful descriptive string
* in context of operators such as LogicalNot. Native PHPUnit constraints
* are supported out of the box by LogicalNot, but externally developed
* ones had no way to provide correct strings in this context.
*
* The method shall return empty string, when it does not handle
* customization by itself.
*
* @param Operator $operator the $operator of the expression
* @param mixed $role role of $this constraint in the $operator expression
*/
protected function toStringInContext(Operator $operator, $role): string
{
return '';
}
/**
* Returns the description of the failure when this constraint appears in
* context of an $operator expression.
*
* The purpose of this method is to provide meaningful failure description
* in context of operators such as LogicalNot. Native PHPUnit constraints
* are supported out of the box by LogicalNot, but externally developed
* ones had no way to provide correct messages in this context.
*
* The method shall return empty string, when it does not handle
* customization by itself.
*
* @param Operator $operator the $operator of the expression
* @param mixed $role role of $this constraint in the $operator expression
* @param mixed $other evaluated value or object
*/
protected function failureDescriptionInContext(Operator $operator, $role, $other): string
{
$string = $this->toStringInContext($operator, $role);
if ($string === '') {
return '';
}
return $this->exporter()->export($other) . ' ' . $string;
}
/**
* Reduces the sub-expression starting at $this by skipping degenerate
* sub-expression and returns first descendant constraint that starts
* a non-reducible sub-expression.
*
* Returns $this for terminal constraints and for operators that start
* non-reducible sub-expression, or the nearest descendant of $this that
* starts a non-reducible sub-expression.
*
* A constraint expression may be modelled as a tree with non-terminal
* nodes (operators) and terminal nodes. For example:
*
* LogicalOr (operator, non-terminal)
* + LogicalAnd (operator, non-terminal)
* | + IsType('int') (terminal)
* | + GreaterThan(10) (terminal)
* + LogicalNot (operator, non-terminal)
* + IsType('array') (terminal)
*
* A degenerate sub-expression is a part of the tree, that effectively does
* not contribute to the evaluation of the expression it appears in. An example
* of degenerate sub-expression is a BinaryOperator constructed with single
* operand or nested BinaryOperators, each with single operand. An
* expression involving a degenerate sub-expression is equivalent to a
* reduced expression with the degenerate sub-expression removed, for example
*
* LogicalAnd (operator)
* + LogicalOr (degenerate operator)
* | + LogicalAnd (degenerate operator)
* | + IsType('int') (terminal)
* + GreaterThan(10) (terminal)
*
* is equivalent to
*
* LogicalAnd (operator)
* + IsType('int') (terminal)
* + GreaterThan(10) (terminal)
*
* because the subexpression
*
* + LogicalOr
* + LogicalAnd
* + -
*
* is degenerate. Calling reduce() on the LogicalOr object above, as well
* as on LogicalAnd, shall return the IsType('int') instance.
*
* Other specific reductions can be implemented, for example cascade of
* LogicalNot operators
*
* + LogicalNot
* + LogicalNot
* +LogicalNot
* + IsTrue
*
* can be reduced to
*
* LogicalNot
* + IsTrue
*/
protected function reduce(): self
{
return $this;
}
}
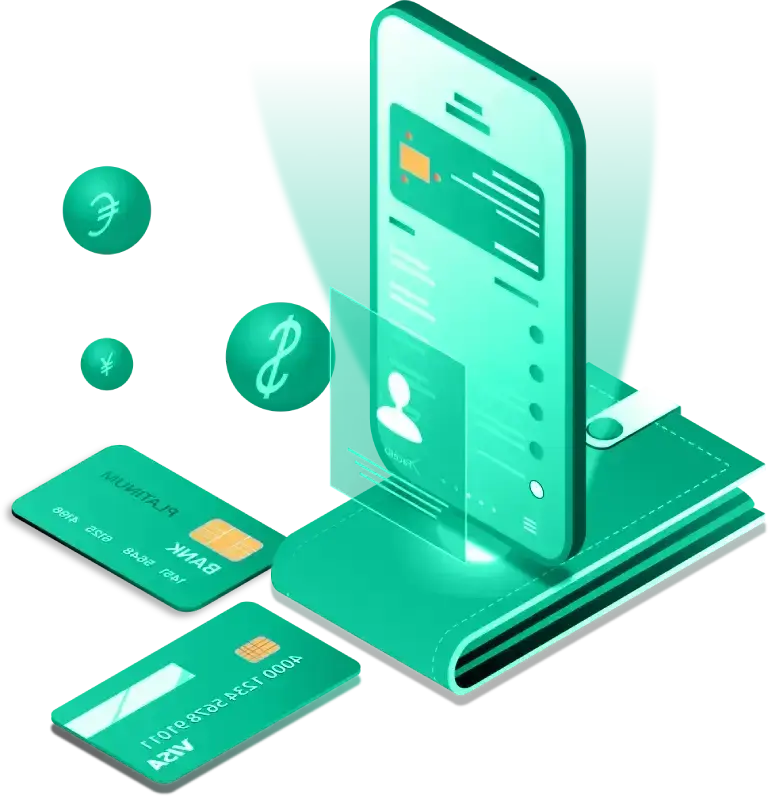
How it Works

Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
