Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
/*
* This file is part of the Symfony package.
*
* (c) Fabien Potencier <fabien@symfony.com>
*
* For the full copyright and license information, please view the LICENSE
* file that was distributed with this source code.
*/
/*
* This code is partially based on the Rack-Cache library by Ryan Tomayko,
* which is released under the MIT license.
* (based on commit 02d2b48d75bcb63cf1c0c7149c077ad256542801)
*/
namespace Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpCache;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernelInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\TerminableInterface;
/**
* Cache provides HTTP caching.
*
* @author Fabien Potencier <fabien@symfony.com>
*/
class HttpCache implements HttpKernelInterface, TerminableInterface
{
private $kernel;
private $store;
private $request;
private $surrogate;
private $surrogateCacheStrategy = null;
private array $options = [];
private array $traces = [];
/**
* Constructor.
*
* The available options are:
*
* * debug If true, exceptions are thrown when things go wrong. Otherwise, the cache
* will try to carry on and deliver a meaningful response.
*
* * trace_level May be one of 'none', 'short' and 'full'. For 'short', a concise trace of the
* main request will be added as an HTTP header. 'full' will add traces for all
* requests (including ESI subrequests). (default: 'full' if in debug; 'none' otherwise)
*
* * trace_header Header name to use for traces. (default: X-Symfony-Cache)
*
* * default_ttl The number of seconds that a cache entry should be considered
* fresh when no explicit freshness information is provided in
* a response. Explicit Cache-Control or Expires headers
* override this value. (default: 0)
*
* * private_headers Set of request headers that trigger "private" cache-control behavior
* on responses that don't explicitly state whether the response is
* public or private via a Cache-Control directive. (default: Authorization and Cookie)
*
* * allow_reload Specifies whether the client can force a cache reload by including a
* Cache-Control "no-cache" directive in the request. Set it to ``true``
* for compliance with RFC 2616. (default: false)
*
* * allow_revalidate Specifies whether the client can force a cache revalidate by including
* a Cache-Control "max-age=0" directive in the request. Set it to ``true``
* for compliance with RFC 2616. (default: false)
*
* * stale_while_revalidate Specifies the default number of seconds (the granularity is the second as the
* Response TTL precision is a second) during which the cache can immediately return
* a stale response while it revalidates it in the background (default: 2).
* This setting is overridden by the stale-while-revalidate HTTP Cache-Control
* extension (see RFC 5861).
*
* * stale_if_error Specifies the default number of seconds (the granularity is the second) during which
* the cache can serve a stale response when an error is encountered (default: 60).
* This setting is overridden by the stale-if-error HTTP Cache-Control extension
* (see RFC 5861).
*/
public function __construct(HttpKernelInterface $kernel, StoreInterface $store, SurrogateInterface $surrogate = null, array $options = [])
{
$this->store = $store;
$this->kernel = $kernel;
$this->surrogate = $surrogate;
// needed in case there is a fatal error because the backend is too slow to respond
register_shutdown_function([$this->store, 'cleanup']);
$this->options = array_merge([
'debug' => false,
'default_ttl' => 0,
'private_headers' => ['Authorization', 'Cookie'],
'allow_reload' => false,
'allow_revalidate' => false,
'stale_while_revalidate' => 2,
'stale_if_error' => 60,
'trace_level' => 'none',
'trace_header' => 'X-Symfony-Cache',
], $options);
if (!isset($options['trace_level'])) {
$this->options['trace_level'] = $this->options['debug'] ? 'full' : 'none';
}
}
/**
* Gets the current store.
*/
public function getStore(): StoreInterface
{
return $this->store;
}
/**
* Returns an array of events that took place during processing of the last request.
*/
public function getTraces(): array
{
return $this->traces;
}
private function addTraces(Response $response)
{
$traceString = null;
if ('full' === $this->options['trace_level']) {
$traceString = $this->getLog();
}
if ('short' === $this->options['trace_level'] && $masterId = array_key_first($this->traces)) {
$traceString = implode('/', $this->traces[$masterId]);
}
if (null !== $traceString) {
$response->headers->add([$this->options['trace_header'] => $traceString]);
}
}
/**
* Returns a log message for the events of the last request processing.
*/
public function getLog(): string
{
$log = [];
foreach ($this->traces as $request => $traces) {
$log[] = sprintf('%s: %s', $request, implode(', ', $traces));
}
return implode('; ', $log);
}
/**
* Gets the Request instance associated with the main request.
*/
public function getRequest(): Request
{
return $this->request;
}
/**
* Gets the Kernel instance.
*/
public function getKernel(): HttpKernelInterface
{
return $this->kernel;
}
/**
* Gets the Surrogate instance.
*
* @throws \LogicException
*/
public function getSurrogate(): SurrogateInterface
{
return $this->surrogate;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function handle(Request $request, int $type = HttpKernelInterface::MAIN_REQUEST, bool $catch = true): Response
{
// FIXME: catch exceptions and implement a 500 error page here? -> in Varnish, there is a built-in error page mechanism
if (HttpKernelInterface::MAIN_REQUEST === $type) {
$this->traces = [];
// Keep a clone of the original request for surrogates so they can access it.
// We must clone here to get a separate instance because the application will modify the request during
// the application flow (we know it always does because we do ourselves by setting REMOTE_ADDR to 127.0.0.1
// and adding the X-Forwarded-For header, see HttpCache::forward()).
$this->request = clone $request;
if (null !== $this->surrogate) {
$this->surrogateCacheStrategy = $this->surrogate->createCacheStrategy();
}
}
$this->traces[$this->getTraceKey($request)] = [];
if (!$request->isMethodSafe()) {
$response = $this->invalidate($request, $catch);
} elseif ($request->headers->has('expect') || !$request->isMethodCacheable()) {
$response = $this->pass($request, $catch);
} elseif ($this->options['allow_reload'] && $request->isNoCache()) {
/*
If allow_reload is configured and the client requests "Cache-Control: no-cache",
reload the cache by fetching a fresh response and caching it (if possible).
*/
$this->record($request, 'reload');
$response = $this->fetch($request, $catch);
} else {
$response = $this->lookup($request, $catch);
}
$this->restoreResponseBody($request, $response);
if (HttpKernelInterface::MAIN_REQUEST === $type) {
$this->addTraces($response);
}
if (null !== $this->surrogate) {
if (HttpKernelInterface::MAIN_REQUEST === $type) {
$this->surrogateCacheStrategy->update($response);
} else {
$this->surrogateCacheStrategy->add($response);
}
}
$response->prepare($request);
$response->isNotModified($request);
return $response;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function terminate(Request $request, Response $response)
{
if ($this->getKernel() instanceof TerminableInterface) {
$this->getKernel()->terminate($request, $response);
}
}
/**
* Forwards the Request to the backend without storing the Response in the cache.
*
* @param bool $catch Whether to process exceptions
*/
protected function pass(Request $request, bool $catch = false): Response
{
$this->record($request, 'pass');
return $this->forward($request, $catch);
}
/**
* Invalidates non-safe methods (like POST, PUT, and DELETE).
*
* @param bool $catch Whether to process exceptions
*
* @throws \Exception
*
* @see RFC2616 13.10
*/
protected function invalidate(Request $request, bool $catch = false): Response
{
$response = $this->pass($request, $catch);
// invalidate only when the response is successful
if ($response->isSuccessful() || $response->isRedirect()) {
try {
$this->store->invalidate($request);
// As per the RFC, invalidate Location and Content-Location URLs if present
foreach (['Location', 'Content-Location'] as $header) {
if ($uri = $response->headers->get($header)) {
$subRequest = Request::create($uri, 'get', [], [], [], $request->server->all());
$this->store->invalidate($subRequest);
}
}
$this->record($request, 'invalidate');
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$this->record($request, 'invalidate-failed');
if ($this->options['debug']) {
throw $e;
}
}
}
return $response;
}
/**
* Lookups a Response from the cache for the given Request.
*
* When a matching cache entry is found and is fresh, it uses it as the
* response without forwarding any request to the backend. When a matching
* cache entry is found but is stale, it attempts to "validate" the entry with
* the backend using conditional GET. When no matching cache entry is found,
* it triggers "miss" processing.
*
* @param bool $catch Whether to process exceptions
*
* @throws \Exception
*/
protected function lookup(Request $request, bool $catch = false): Response
{
try {
$entry = $this->store->lookup($request);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$this->record($request, 'lookup-failed');
if ($this->options['debug']) {
throw $e;
}
return $this->pass($request, $catch);
}
if (null === $entry) {
$this->record($request, 'miss');
return $this->fetch($request, $catch);
}
if (!$this->isFreshEnough($request, $entry)) {
$this->record($request, 'stale');
return $this->validate($request, $entry, $catch);
}
if ($entry->headers->hasCacheControlDirective('no-cache')) {
return $this->validate($request, $entry, $catch);
}
$this->record($request, 'fresh');
$entry->headers->set('Age', $entry->getAge());
return $entry;
}
/**
* Validates that a cache entry is fresh.
*
* The original request is used as a template for a conditional
* GET request with the backend.
*
* @param bool $catch Whether to process exceptions
*/
protected function validate(Request $request, Response $entry, bool $catch = false): Response
{
$subRequest = clone $request;
// send no head requests because we want content
if ('HEAD' === $request->getMethod()) {
$subRequest->setMethod('GET');
}
// add our cached last-modified validator
if ($entry->headers->has('Last-Modified')) {
$subRequest->headers->set('If-Modified-Since', $entry->headers->get('Last-Modified'));
}
// Add our cached etag validator to the environment.
// We keep the etags from the client to handle the case when the client
// has a different private valid entry which is not cached here.
$cachedEtags = $entry->getEtag() ? [$entry->getEtag()] : [];
$requestEtags = $request->getETags();
if ($etags = array_unique(array_merge($cachedEtags, $requestEtags))) {
$subRequest->headers->set('If-None-Match', implode(', ', $etags));
}
$response = $this->forward($subRequest, $catch, $entry);
if (304 == $response->getStatusCode()) {
$this->record($request, 'valid');
// return the response and not the cache entry if the response is valid but not cached
$etag = $response->getEtag();
if ($etag && \in_array($etag, $requestEtags) && !\in_array($etag, $cachedEtags)) {
return $response;
}
$entry = clone $entry;
$entry->headers->remove('Date');
foreach (['Date', 'Expires', 'Cache-Control', 'ETag', 'Last-Modified'] as $name) {
if ($response->headers->has($name)) {
$entry->headers->set($name, $response->headers->get($name));
}
}
$response = $entry;
} else {
$this->record($request, 'invalid');
}
if ($response->isCacheable()) {
$this->store($request, $response);
}
return $response;
}
/**
* Unconditionally fetches a fresh response from the backend and
* stores it in the cache if is cacheable.
*
* @param bool $catch Whether to process exceptions
*/
protected function fetch(Request $request, bool $catch = false): Response
{
$subRequest = clone $request;
// send no head requests because we want content
if ('HEAD' === $request->getMethod()) {
$subRequest->setMethod('GET');
}
// avoid that the backend sends no content
$subRequest->headers->remove('If-Modified-Since');
$subRequest->headers->remove('If-None-Match');
$response = $this->forward($subRequest, $catch);
if ($response->isCacheable()) {
$this->store($request, $response);
}
return $response;
}
/**
* Forwards the Request to the backend and returns the Response.
*
* All backend requests (cache passes, fetches, cache validations)
* run through this method.
*
* @param bool $catch Whether to catch exceptions or not
* @param Response|null $entry A Response instance (the stale entry if present, null otherwise)
*
* @return Response
*/
protected function forward(Request $request, bool $catch = false, Response $entry = null)
{
if ($this->surrogate) {
$this->surrogate->addSurrogateCapability($request);
}
// always a "master" request (as the real master request can be in cache)
$response = SubRequestHandler::handle($this->kernel, $request, HttpKernelInterface::MAIN_REQUEST, $catch);
/*
* Support stale-if-error given on Responses or as a config option.
* RFC 7234 summarizes in Section 4.2.4 (but also mentions with the individual
* Cache-Control directives) that
*
* A cache MUST NOT generate a stale response if it is prohibited by an
* explicit in-protocol directive (e.g., by a "no-store" or "no-cache"
* cache directive, a "must-revalidate" cache-response-directive, or an
* applicable "s-maxage" or "proxy-revalidate" cache-response-directive;
* see Section 5.2.2).
*
* https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-4.2.4
*
* We deviate from this in one detail, namely that we *do* serve entries in the
* stale-if-error case even if they have a `s-maxage` Cache-Control directive.
*/
if (null !== $entry
&& \in_array($response->getStatusCode(), [500, 502, 503, 504])
&& !$entry->headers->hasCacheControlDirective('no-cache')
&& !$entry->mustRevalidate()
) {
if (null === $age = $entry->headers->getCacheControlDirective('stale-if-error')) {
$age = $this->options['stale_if_error'];
}
/*
* stale-if-error gives the (extra) time that the Response may be used *after* it has become stale.
* So we compare the time the $entry has been sitting in the cache already with the
* time it was fresh plus the allowed grace period.
*/
if ($entry->getAge() <= $entry->getMaxAge() + $age) {
$this->record($request, 'stale-if-error');
return $entry;
}
}
/*
RFC 7231 Sect. 7.1.1.2 says that a server that does not have a reasonably accurate
clock MUST NOT send a "Date" header, although it MUST send one in most other cases
except for 1xx or 5xx responses where it MAY do so.
Anyway, a client that received a message without a "Date" header MUST add it.
*/
if (!$response->headers->has('Date')) {
$response->setDate(\DateTime::createFromFormat('U', time()));
}
$this->processResponseBody($request, $response);
if ($this->isPrivateRequest($request) && !$response->headers->hasCacheControlDirective('public')) {
$response->setPrivate();
} elseif ($this->options['default_ttl'] > 0 && null === $response->getTtl() && !$response->headers->getCacheControlDirective('must-revalidate')) {
$response->setTtl($this->options['default_ttl']);
}
return $response;
}
/**
* Checks whether the cache entry is "fresh enough" to satisfy the Request.
*/
protected function isFreshEnough(Request $request, Response $entry): bool
{
if (!$entry->isFresh()) {
return $this->lock($request, $entry);
}
if ($this->options['allow_revalidate'] && null !== $maxAge = $request->headers->getCacheControlDirective('max-age')) {
return $maxAge > 0 && $maxAge >= $entry->getAge();
}
return true;
}
/**
* Locks a Request during the call to the backend.
*
* @return bool true if the cache entry can be returned even if it is staled, false otherwise
*/
protected function lock(Request $request, Response $entry): bool
{
// try to acquire a lock to call the backend
$lock = $this->store->lock($request);
if (true === $lock) {
// we have the lock, call the backend
return false;
}
// there is already another process calling the backend
// May we serve a stale response?
if ($this->mayServeStaleWhileRevalidate($entry)) {
$this->record($request, 'stale-while-revalidate');
return true;
}
// wait for the lock to be released
if ($this->waitForLock($request)) {
// replace the current entry with the fresh one
$new = $this->lookup($request);
$entry->headers = $new->headers;
$entry->setContent($new->getContent());
$entry->setStatusCode($new->getStatusCode());
$entry->setProtocolVersion($new->getProtocolVersion());
foreach ($new->headers->getCookies() as $cookie) {
$entry->headers->setCookie($cookie);
}
} else {
// backend is slow as hell, send a 503 response (to avoid the dog pile effect)
$entry->setStatusCode(503);
$entry->setContent('503 Service Unavailable');
$entry->headers->set('Retry-After', 10);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Writes the Response to the cache.
*
* @throws \Exception
*/
protected function store(Request $request, Response $response)
{
try {
$this->store->write($request, $response);
$this->record($request, 'store');
$response->headers->set('Age', $response->getAge());
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$this->record($request, 'store-failed');
if ($this->options['debug']) {
throw $e;
}
}
// now that the response is cached, release the lock
$this->store->unlock($request);
}
/**
* Restores the Response body.
*/
private function restoreResponseBody(Request $request, Response $response)
{
if ($response->headers->has('X-Body-Eval')) {
ob_start();
if ($response->headers->has('X-Body-File')) {
include $response->headers->get('X-Body-File');
} else {
eval('; ?>'.$response->getContent().'<?php ;');
}
$response->setContent(ob_get_clean());
$response->headers->remove('X-Body-Eval');
if (!$response->headers->has('Transfer-Encoding')) {
$response->headers->set('Content-Length', \strlen($response->getContent()));
}
} elseif ($response->headers->has('X-Body-File')) {
// Response does not include possibly dynamic content (ESI, SSI), so we need
// not handle the content for HEAD requests
if (!$request->isMethod('HEAD')) {
$response->setContent(file_get_contents($response->headers->get('X-Body-File')));
}
} else {
return;
}
$response->headers->remove('X-Body-File');
}
protected function processResponseBody(Request $request, Response $response)
{
if (null !== $this->surrogate && $this->surrogate->needsParsing($response)) {
$this->surrogate->process($request, $response);
}
}
/**
* Checks if the Request includes authorization or other sensitive information
* that should cause the Response to be considered private by default.
*/
private function isPrivateRequest(Request $request): bool
{
foreach ($this->options['private_headers'] as $key) {
$key = strtolower(str_replace('HTTP_', '', $key));
if ('cookie' === $key) {
if (\count($request->cookies->all())) {
return true;
}
} elseif ($request->headers->has($key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Records that an event took place.
*/
private function record(Request $request, string $event)
{
$this->traces[$this->getTraceKey($request)][] = $event;
}
/**
* Calculates the key we use in the "trace" array for a given request.
*/
private function getTraceKey(Request $request): string
{
$path = $request->getPathInfo();
if ($qs = $request->getQueryString()) {
$path .= '?'.$qs;
}
return $request->getMethod().' '.$path;
}
/**
* Checks whether the given (cached) response may be served as "stale" when a revalidation
* is currently in progress.
*/
private function mayServeStaleWhileRevalidate(Response $entry): bool
{
$timeout = $entry->headers->getCacheControlDirective('stale-while-revalidate');
if (null === $timeout) {
$timeout = $this->options['stale_while_revalidate'];
}
return abs($entry->getTtl() ?? 0) < $timeout;
}
/**
* Waits for the store to release a locked entry.
*/
private function waitForLock(Request $request): bool
{
$wait = 0;
while ($this->store->isLocked($request) && $wait < 100) {
usleep(50000);
++$wait;
}
return $wait < 100;
}
}
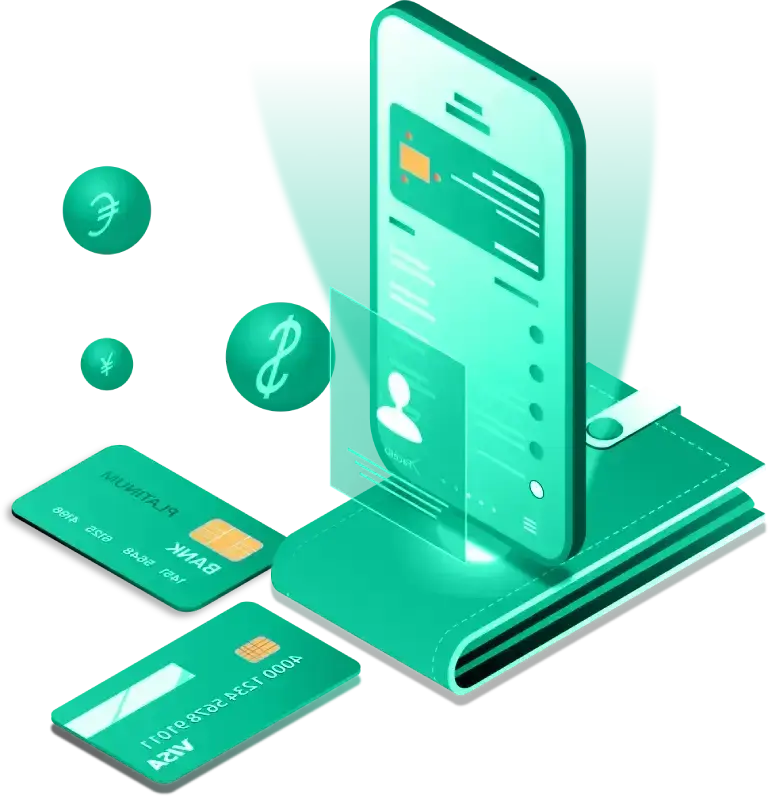
How it Works

Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
