Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
/**
* This file is part of the ramsey/collection library
*
* For the full copyright and license information, please view the LICENSE
* file that was distributed with this source code.
*
* @copyright Copyright (c) Ben Ramsey <ben@benramsey.com>
* @license http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT MIT
*/
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace Ramsey\Collection;
use Ramsey\Collection\Exception\NoSuchElementException;
use RuntimeException;
/**
* A linear collection that supports element insertion and removal at both ends.
*
* Most `DoubleEndedQueueInterface` implementations place no fixed limits on the
* number of elements they may contain, but this interface supports
* capacity-restricted double-ended queues as well as those with no fixed size
* limit.
*
* This interface defines methods to access the elements at both ends of the
* double-ended queue. Methods are provided to insert, remove, and examine the
* element. Each of these methods exists in two forms: one throws an exception
* if the operation fails, the other returns a special value (either `null` or
* `false`, depending on the operation). The latter form of the insert operation
* is designed specifically for use with capacity-restricted implementations; in
* most implementations, insert operations cannot fail.
*
* The twelve methods described above are summarized in the following table:
*
* <table>
* <caption>Summary of DoubleEndedQueueInterface methods</caption>
* <thead>
* <tr>
* <th></th>
* <th colspan=2>First Element (Head)</th>
* <th colspan=2>Last Element (Tail)</th>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td></td>
* <td><em>Throws exception</em></td>
* <td><em>Special value</em></td>
* <td><em>Throws exception</em></td>
* <td><em>Special value</em></td>
* </tr>
* </thead>
* <tbody>
* <tr>
* <th>Insert</th>
* <td><code>addFirst()</code></td>
* <td><code>offerFirst()</code></td>
* <td><code>addLast()</code></td>
* <td><code>offerLast()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <th>Remove</th>
* <td><code>removeFirst()</code></td>
* <td><code>pollFirst()</code></td>
* <td><code>removeLast()</code></td>
* <td><code>pollLast()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <th>Examine</th>
* <td><code>firstElement()</code></td>
* <td><code>peekFirst()</code></td>
* <td><code>lastElement()</code></td>
* <td><code>peekLast()</code></td>
* </tr>
* </tbody>
* </table>
*
* This interface extends the `QueueInterface`. When a double-ended queue is
* used as a queue, FIFO (first-in-first-out) behavior results. Elements are
* added at the end of the double-ended queue and removed from the beginning.
* The methods inherited from the `QueueInterface` are precisely equivalent to
* `DoubleEndedQueueInterface` methods as indicated in the following table:
*
* <table>
* <caption>Comparison of QueueInterface and DoubleEndedQueueInterface methods</caption>
* <thead>
* <tr>
* <th>QueueInterface Method</th>
* <th>DoubleEndedQueueInterface Method</th>
* </tr>
* </thead>
* <tbody>
* <tr>
* <td><code>add()</code></td>
* <td><code>addLast()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><code>offer()</code></td>
* <td><code>offerLast()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><code>remove()</code></td>
* <td><code>removeFirst()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><code>poll()</code></td>
* <td><code>pollFirst()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><code>element()</code></td>
* <td><code>firstElement()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><code>peek()</code></td>
* <td><code>peekFirst()</code></td>
* </tr>
* </tbody>
* </table>
*
* Double-ended queues can also be used as LIFO (last-in-first-out) stacks. When
* a double-ended queue is used as a stack, elements are pushed and popped from
* the beginning of the double-ended queue. Stack concepts are precisely
* equivalent to `DoubleEndedQueueInterface` methods as indicated in the table
* below:
*
* <table>
* <caption>Comparison of stack concepts and DoubleEndedQueueInterface methods</caption>
* <thead>
* <tr>
* <th>Stack concept</th>
* <th>DoubleEndedQueueInterface Method</th>
* </tr>
* </thead>
* <tbody>
* <tr>
* <td><em>push</em></td>
* <td><code>addFirst()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><em>pop</em></td>
* <td><code>removeFirst()</code></td>
* </tr>
* <tr>
* <td><em>peek</em></td>
* <td><code>peekFirst()</code></td>
* </tr>
* </tbody>
* </table>
*
* Note that the `peek()` method works equally well when a double-ended queue is
* used as a queue or a stack; in either case, elements are drawn from the
* beginning of the double-ended queue.
*
* While `DoubleEndedQueueInterface` implementations are not strictly required
* to prohibit the insertion of `null` elements, they are strongly encouraged to
* do so. Users of any `DoubleEndedQueueInterface` implementations that do allow
* `null` elements are strongly encouraged *not* to take advantage of the
* ability to insert nulls. This is so because `null` is used as a special
* return value by various methods to indicated that the double-ended queue is
* empty.
*
* @template T
* @extends QueueInterface<T>
*/
interface DoubleEndedQueueInterface extends QueueInterface
{
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this queue if it is
* possible to do so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.
*
* When using a capacity-restricted double-ended queue, it is generally
* preferable to use the `offerFirst()` method.
*
* @param T $element The element to add to the front of this queue.
*
* @return bool `true` if this queue changed as a result of the call.
*
* @throws RuntimeException if a queue refuses to add a particular element
* for any reason other than that it already contains the element.
* Implementations should use a more-specific exception that extends
* `\RuntimeException`.
*/
// phpcs:ignore SlevomatCodingStandard.TypeHints.ParameterTypeHint.MissingNativeTypeHint
public function addFirst($element): bool;
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this queue if it is possible
* to do so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.
*
* When using a capacity-restricted double-ended queue, it is generally
* preferable to use the `offerLast()` method.
*
* This method is equivalent to `add()`.
*
* @param T $element The element to add to the end of this queue.
*
* @return bool `true` if this queue changed as a result of the call.
*
* @throws RuntimeException if a queue refuses to add a particular element
* for any reason other than that it already contains the element.
* Implementations should use a more-specific exception that extends
* `\RuntimeException`.
*/
// phpcs:ignore SlevomatCodingStandard.TypeHints.ParameterTypeHint.MissingNativeTypeHint
public function addLast($element): bool;
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this queue if it is
* possible to do so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.
*
* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally
* preferable to `addFirst()`, which can fail to insert an element only by
* throwing an exception.
*
* @param T $element The element to add to the front of this queue.
*
* @return bool `true` if the element was added to this queue, else `false`.
*/
// phpcs:ignore SlevomatCodingStandard.TypeHints.ParameterTypeHint.MissingNativeTypeHint
public function offerFirst($element): bool;
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this queue if it is possible
* to do so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.
*
* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally
* preferable to `addLast()` which can fail to insert an element only by
* throwing an exception.
*
* @param T $element The element to add to the end of this queue.
*
* @return bool `true` if the element was added to this queue, else `false`.
*/
// phpcs:ignore SlevomatCodingStandard.TypeHints.ParameterTypeHint.MissingNativeTypeHint
public function offerLast($element): bool;
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue.
*
* This method differs from `pollFirst()` only in that it throws an
* exception if this queue is empty.
*
* @return T the first element in this queue.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty.
*/
public function removeFirst();
/**
* Retrieves and removes the tail of this queue.
*
* This method differs from `pollLast()` only in that it throws an exception
* if this queue is empty.
*
* @return T the last element in this queue.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty.
*/
public function removeLast();
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns `null` if this
* queue is empty.
*
* @return T|null the head of this queue, or `null` if this queue is empty.
*/
public function pollFirst();
/**
* Retrieves and removes the tail of this queue, or returns `null` if this
* queue is empty.
*
* @return T|null the tail of this queue, or `null` if this queue is empty.
*/
public function pollLast();
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue.
*
* This method differs from `peekFirst()` only in that it throws an
* exception if this queue is empty.
*
* @return T the head of this queue.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty.
*/
public function firstElement();
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the tail of this queue.
*
* This method differs from `peekLast()` only in that it throws an exception
* if this queue is empty.
*
* @return T the tail of this queue.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty.
*/
public function lastElement();
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns `null`
* if this queue is empty.
*
* @return T|null the head of this queue, or `null` if this queue is empty.
*/
public function peekFirst();
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the tail of this queue, or returns `null`
* if this queue is empty.
*
* @return T|null the tail of this queue, or `null` if this queue is empty.
*/
public function peekLast();
}
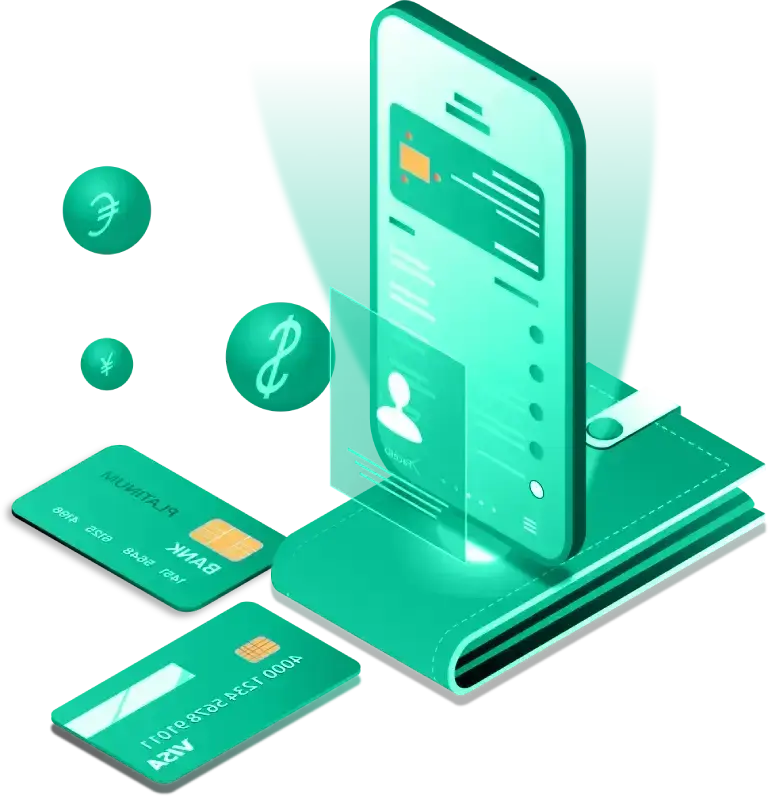
How it Works

Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
