Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
namespace PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Cell;
use PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Calculation\Functions;
use PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Exception;
use PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Worksheet\Worksheet;
/**
* Helper class to manipulate cell coordinates.
*
* Columns indexes and rows are always based on 1, **not** on 0. This match the behavior
* that Excel users are used to, and also match the Excel functions `COLUMN()` and `ROW()`.
*/
abstract class Coordinate
{
public const A1_COORDINATE_REGEX = '/^(?<col>\$?[A-Z]{1,3})(?<row>\$?\d{1,7})$/i';
/**
* Default range variable constant.
*
* @var string
*/
const DEFAULT_RANGE = 'A1:A1';
/**
* Convert string coordinate to [0 => int column index, 1 => int row index].
*
* @param string $cellAddress eg: 'A1'
*
* @return array{0: string, 1: string} Array containing column and row (indexes 0 and 1)
*/
public static function coordinateFromString($cellAddress): array
{
if (preg_match(self::A1_COORDINATE_REGEX, $cellAddress, $matches)) {
return [$matches['col'], $matches['row']];
} elseif (self::coordinateIsRange($cellAddress)) {
throw new Exception('Cell coordinate string can not be a range of cells');
} elseif ($cellAddress == '') {
throw new Exception('Cell coordinate can not be zero-length string');
}
throw new Exception('Invalid cell coordinate ' . $cellAddress);
}
/**
* Convert string coordinate to [0 => int column index, 1 => int row index, 2 => string column string].
*
* @param string $coordinates eg: 'A1', '$B$12'
*
* @return array{0: int, 1: int, 2: string} Array containing column and row index, and column string
*/
public static function indexesFromString(string $coordinates): array
{
[$column, $row] = self::coordinateFromString($coordinates);
$column = ltrim($column, '$');
return [
self::columnIndexFromString($column),
(int) ltrim($row, '$'),
$column,
];
}
/**
* Checks if a Cell Address represents a range of cells.
*
* @param string $cellAddress eg: 'A1' or 'A1:A2' or 'A1:A2,C1:C2'
*
* @return bool Whether the coordinate represents a range of cells
*/
public static function coordinateIsRange($cellAddress)
{
return (strpos($cellAddress, ':') !== false) || (strpos($cellAddress, ',') !== false);
}
/**
* Make string row, column or cell coordinate absolute.
*
* @param string $cellAddress e.g. 'A' or '1' or 'A1'
* Note that this value can be a row or column reference as well as a cell reference
*
* @return string Absolute coordinate e.g. '$A' or '$1' or '$A$1'
*/
public static function absoluteReference($cellAddress)
{
if (self::coordinateIsRange($cellAddress)) {
throw new Exception('Cell coordinate string can not be a range of cells');
}
// Split out any worksheet name from the reference
[$worksheet, $cellAddress] = Worksheet::extractSheetTitle($cellAddress, true);
if ($worksheet > '') {
$worksheet .= '!';
}
// Create absolute coordinate
$cellAddress = "$cellAddress";
if (ctype_digit($cellAddress)) {
return $worksheet . '$' . $cellAddress;
} elseif (ctype_alpha($cellAddress)) {
return $worksheet . '$' . strtoupper($cellAddress);
}
return $worksheet . self::absoluteCoordinate($cellAddress);
}
/**
* Make string coordinate absolute.
*
* @param string $cellAddress e.g. 'A1'
*
* @return string Absolute coordinate e.g. '$A$1'
*/
public static function absoluteCoordinate($cellAddress)
{
if (self::coordinateIsRange($cellAddress)) {
throw new Exception('Cell coordinate string can not be a range of cells');
}
// Split out any worksheet name from the coordinate
[$worksheet, $cellAddress] = Worksheet::extractSheetTitle($cellAddress, true);
if ($worksheet > '') {
$worksheet .= '!';
}
// Create absolute coordinate
[$column, $row] = self::coordinateFromString($cellAddress);
$column = ltrim($column, '$');
$row = ltrim($row, '$');
return $worksheet . '$' . $column . '$' . $row;
}
/**
* Split range into coordinate strings.
*
* @param string $range e.g. 'B4:D9' or 'B4:D9,H2:O11' or 'B4'
*
* @return array Array containing one or more arrays containing one or two coordinate strings
* e.g. ['B4','D9'] or [['B4','D9'], ['H2','O11']]
* or ['B4']
*/
public static function splitRange($range)
{
// Ensure $pRange is a valid range
if (empty($range)) {
$range = self::DEFAULT_RANGE;
}
$exploded = explode(',', $range);
$counter = count($exploded);
for ($i = 0; $i < $counter; ++$i) {
// @phpstan-ignore-next-line
$exploded[$i] = explode(':', $exploded[$i]);
}
return $exploded;
}
/**
* Build range from coordinate strings.
*
* @param array $range Array containing one or more arrays containing one or two coordinate strings
*
* @return string String representation of $pRange
*/
public static function buildRange(array $range)
{
// Verify range
if (empty($range) || !is_array($range[0])) {
throw new Exception('Range does not contain any information');
}
// Build range
$counter = count($range);
for ($i = 0; $i < $counter; ++$i) {
$range[$i] = implode(':', $range[$i]);
}
return implode(',', $range);
}
/**
* Calculate range boundaries.
*
* @param string $range Cell range, Single Cell, Row/Column Range (e.g. A1:A1, B2, B:C, 2:3)
*
* @return array Range coordinates [Start Cell, End Cell]
* where Start Cell and End Cell are arrays (Column Number, Row Number)
*/
public static function rangeBoundaries(string $range): array
{
// Ensure $pRange is a valid range
if (empty($range)) {
$range = self::DEFAULT_RANGE;
}
// Uppercase coordinate
$range = strtoupper($range);
// Extract range
if (strpos($range, ':') === false) {
$rangeA = $rangeB = $range;
} else {
[$rangeA, $rangeB] = explode(':', $range);
}
if (is_numeric($rangeA) && is_numeric($rangeB)) {
$rangeA = 'A' . $rangeA;
$rangeB = AddressRange::MAX_COLUMN . $rangeB;
}
if (ctype_alpha($rangeA) && ctype_alpha($rangeB)) {
$rangeA = $rangeA . '1';
$rangeB = $rangeB . AddressRange::MAX_ROW;
}
// Calculate range outer borders
$rangeStart = self::coordinateFromString($rangeA);
$rangeEnd = self::coordinateFromString($rangeB);
// Translate column into index
$rangeStart[0] = self::columnIndexFromString($rangeStart[0]);
$rangeEnd[0] = self::columnIndexFromString($rangeEnd[0]);
return [$rangeStart, $rangeEnd];
}
/**
* Calculate range dimension.
*
* @param string $range Cell range, Single Cell, Row/Column Range (e.g. A1:A1, B2, B:C, 2:3)
*
* @return array Range dimension (width, height)
*/
public static function rangeDimension($range)
{
// Calculate range outer borders
[$rangeStart, $rangeEnd] = self::rangeBoundaries($range);
return [($rangeEnd[0] - $rangeStart[0] + 1), ($rangeEnd[1] - $rangeStart[1] + 1)];
}
/**
* Calculate range boundaries.
*
* @param string $range Cell range, Single Cell, Row/Column Range (e.g. A1:A1, B2, B:C, 2:3)
*
* @return array Range coordinates [Start Cell, End Cell]
* where Start Cell and End Cell are arrays [Column ID, Row Number]
*/
public static function getRangeBoundaries($range)
{
[$rangeA, $rangeB] = self::rangeBoundaries($range);
return [
[self::stringFromColumnIndex($rangeA[0]), $rangeA[1]],
[self::stringFromColumnIndex($rangeB[0]), $rangeB[1]],
];
}
/**
* Column index from string.
*
* @param ?string $columnAddress eg 'A'
*
* @return int Column index (A = 1)
*/
public static function columnIndexFromString($columnAddress)
{
// Using a lookup cache adds a slight memory overhead, but boosts speed
// caching using a static within the method is faster than a class static,
// though it's additional memory overhead
static $indexCache = [];
$columnAddress = $columnAddress ?? '';
if (isset($indexCache[$columnAddress])) {
return $indexCache[$columnAddress];
}
// It's surprising how costly the strtoupper() and ord() calls actually are, so we use a lookup array
// rather than use ord() and make it case insensitive to get rid of the strtoupper() as well.
// Because it's a static, there's no significant memory overhead either.
static $columnLookup = [
'A' => 1, 'B' => 2, 'C' => 3, 'D' => 4, 'E' => 5, 'F' => 6, 'G' => 7, 'H' => 8, 'I' => 9, 'J' => 10,
'K' => 11, 'L' => 12, 'M' => 13, 'N' => 14, 'O' => 15, 'P' => 16, 'Q' => 17, 'R' => 18, 'S' => 19,
'T' => 20, 'U' => 21, 'V' => 22, 'W' => 23, 'X' => 24, 'Y' => 25, 'Z' => 26,
'a' => 1, 'b' => 2, 'c' => 3, 'd' => 4, 'e' => 5, 'f' => 6, 'g' => 7, 'h' => 8, 'i' => 9, 'j' => 10,
'k' => 11, 'l' => 12, 'm' => 13, 'n' => 14, 'o' => 15, 'p' => 16, 'q' => 17, 'r' => 18, 's' => 19,
't' => 20, 'u' => 21, 'v' => 22, 'w' => 23, 'x' => 24, 'y' => 25, 'z' => 26,
];
// We also use the language construct isset() rather than the more costly strlen() function to match the
// length of $columnAddress for improved performance
if (isset($columnAddress[0])) {
if (!isset($columnAddress[1])) {
$indexCache[$columnAddress] = $columnLookup[$columnAddress];
return $indexCache[$columnAddress];
} elseif (!isset($columnAddress[2])) {
$indexCache[$columnAddress] = $columnLookup[$columnAddress[0]] * 26
+ $columnLookup[$columnAddress[1]];
return $indexCache[$columnAddress];
} elseif (!isset($columnAddress[3])) {
$indexCache[$columnAddress] = $columnLookup[$columnAddress[0]] * 676
+ $columnLookup[$columnAddress[1]] * 26
+ $columnLookup[$columnAddress[2]];
return $indexCache[$columnAddress];
}
}
throw new Exception(
'Column string index can not be ' . ((isset($columnAddress[0])) ? 'longer than 3 characters' : 'empty')
);
}
/**
* String from column index.
*
* @param int $columnIndex Column index (A = 1)
*
* @return string
*/
public static function stringFromColumnIndex($columnIndex)
{
static $indexCache = [];
static $lookupCache = ' ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
if (!isset($indexCache[$columnIndex])) {
$indexValue = $columnIndex;
$base26 = '';
do {
$characterValue = ($indexValue % 26) ?: 26;
$indexValue = ($indexValue - $characterValue) / 26;
$base26 = $lookupCache[$characterValue] . $base26;
} while ($indexValue > 0);
$indexCache[$columnIndex] = $base26;
}
return $indexCache[$columnIndex];
}
/**
* Extract all cell references in range, which may be comprised of multiple cell ranges.
*
* @param string $cellRange Range: e.g. 'A1' or 'A1:C10' or 'A1:E10,A20:E25' or 'A1:E5 C3:G7' or 'A1:C1,A3:C3 B1:C3'
*
* @return array Array containing single cell references
*/
public static function extractAllCellReferencesInRange($cellRange): array
{
if (substr_count($cellRange, '!') > 1) {
throw new Exception('3-D Range References are not supported');
}
[$worksheet, $cellRange] = Worksheet::extractSheetTitle($cellRange, true);
$quoted = '';
if ($worksheet > '') {
$quoted = Worksheet::nameRequiresQuotes($worksheet) ? "'" : '';
if (substr($worksheet, 0, 1) === "'" && substr($worksheet, -1, 1) === "'") {
$worksheet = substr($worksheet, 1, -1);
}
$worksheet = str_replace("'", "''", $worksheet);
}
[$ranges, $operators] = self::getCellBlocksFromRangeString($cellRange);
$cells = [];
foreach ($ranges as $range) {
$cells[] = self::getReferencesForCellBlock($range);
}
$cells = self::processRangeSetOperators($operators, $cells);
if (empty($cells)) {
return [];
}
$cellList = array_merge(...$cells);
return array_map(
function ($cellAddress) use ($worksheet, $quoted) {
return ($worksheet !== '') ? "{$quoted}{$worksheet}{$quoted}!{$cellAddress}" : $cellAddress;
},
self::sortCellReferenceArray($cellList)
);
}
private static function processRangeSetOperators(array $operators, array $cells): array
{
$operatorCount = count($operators);
for ($offset = 0; $offset < $operatorCount; ++$offset) {
$operator = $operators[$offset];
if ($operator !== ' ') {
continue;
}
$cells[$offset] = array_intersect($cells[$offset], $cells[$offset + 1]);
unset($operators[$offset], $cells[$offset + 1]);
$operators = array_values($operators);
$cells = array_values($cells);
--$offset;
--$operatorCount;
}
return $cells;
}
private static function sortCellReferenceArray(array $cellList): array
{
// Sort the result by column and row
$sortKeys = [];
foreach ($cellList as $coordinate) {
$column = '';
$row = 0;
sscanf($coordinate, '%[A-Z]%d', $column, $row);
$key = (--$row * 16384) + self::columnIndexFromString((string) $column);
$sortKeys[$key] = $coordinate;
}
ksort($sortKeys);
return array_values($sortKeys);
}
/**
* Get all cell references for an individual cell block.
*
* @param string $cellBlock A cell range e.g. A4:B5
*
* @return array All individual cells in that range
*/
private static function getReferencesForCellBlock($cellBlock)
{
$returnValue = [];
// Single cell?
if (!self::coordinateIsRange($cellBlock)) {
return (array) $cellBlock;
}
// Range...
$ranges = self::splitRange($cellBlock);
foreach ($ranges as $range) {
// Single cell?
if (!isset($range[1])) {
$returnValue[] = $range[0];
continue;
}
// Range...
[$rangeStart, $rangeEnd] = $range;
[$startColumn, $startRow] = self::coordinateFromString($rangeStart);
[$endColumn, $endRow] = self::coordinateFromString($rangeEnd);
$startColumnIndex = self::columnIndexFromString($startColumn);
$endColumnIndex = self::columnIndexFromString($endColumn);
++$endColumnIndex;
// Current data
$currentColumnIndex = $startColumnIndex;
$currentRow = $startRow;
self::validateRange($cellBlock, $startColumnIndex, $endColumnIndex, (int) $currentRow, (int) $endRow);
// Loop cells
while ($currentColumnIndex < $endColumnIndex) {
while ($currentRow <= $endRow) {
$returnValue[] = self::stringFromColumnIndex($currentColumnIndex) . $currentRow;
++$currentRow;
}
++$currentColumnIndex;
$currentRow = $startRow;
}
}
return $returnValue;
}
/**
* Convert an associative array of single cell coordinates to values to an associative array
* of cell ranges to values. Only adjacent cell coordinates with the same
* value will be merged. If the value is an object, it must implement the method getHashCode().
*
* For example, this function converts:
*
* [ 'A1' => 'x', 'A2' => 'x', 'A3' => 'x', 'A4' => 'y' ]
*
* to:
*
* [ 'A1:A3' => 'x', 'A4' => 'y' ]
*
* @param array $coordinateCollection associative array mapping coordinates to values
*
* @return array associative array mapping coordinate ranges to valuea
*/
public static function mergeRangesInCollection(array $coordinateCollection)
{
$hashedValues = [];
$mergedCoordCollection = [];
foreach ($coordinateCollection as $coord => $value) {
if (self::coordinateIsRange($coord)) {
$mergedCoordCollection[$coord] = $value;
continue;
}
[$column, $row] = self::coordinateFromString($coord);
$row = (int) (ltrim($row, '$'));
$hashCode = $column . '-' . ((is_object($value) && method_exists($value, 'getHashCode')) ? $value->getHashCode() : $value);
if (!isset($hashedValues[$hashCode])) {
$hashedValues[$hashCode] = (object) [
'value' => $value,
'col' => $column,
'rows' => [$row],
];
} else {
$hashedValues[$hashCode]->rows[] = $row;
}
}
ksort($hashedValues);
foreach ($hashedValues as $hashedValue) {
sort($hashedValue->rows);
$rowStart = null;
$rowEnd = null;
$ranges = [];
foreach ($hashedValue->rows as $row) {
if ($rowStart === null) {
$rowStart = $row;
$rowEnd = $row;
} elseif ($rowEnd === $row - 1) {
$rowEnd = $row;
} else {
if ($rowStart == $rowEnd) {
$ranges[] = $hashedValue->col . $rowStart;
} else {
$ranges[] = $hashedValue->col . $rowStart . ':' . $hashedValue->col . $rowEnd;
}
$rowStart = $row;
$rowEnd = $row;
}
}
if ($rowStart !== null) {
if ($rowStart == $rowEnd) {
$ranges[] = $hashedValue->col . $rowStart;
} else {
$ranges[] = $hashedValue->col . $rowStart . ':' . $hashedValue->col . $rowEnd;
}
}
foreach ($ranges as $range) {
$mergedCoordCollection[$range] = $hashedValue->value;
}
}
return $mergedCoordCollection;
}
/**
* Get the individual cell blocks from a range string, removing any $ characters.
* then splitting by operators and returning an array with ranges and operators.
*
* @param string $rangeString
*
* @return array[]
*/
private static function getCellBlocksFromRangeString($rangeString)
{
$rangeString = str_replace('$', '', strtoupper($rangeString));
// split range sets on intersection (space) or union (,) operators
$tokens = preg_split('/([ ,])/', $rangeString, -1, PREG_SPLIT_DELIM_CAPTURE);
/** @phpstan-ignore-next-line */
$split = array_chunk($tokens, 2);
$ranges = array_column($split, 0);
$operators = array_column($split, 1);
return [$ranges, $operators];
}
/**
* Check that the given range is valid, i.e. that the start column and row are not greater than the end column and
* row.
*
* @param string $cellBlock The original range, for displaying a meaningful error message
* @param int $startColumnIndex
* @param int $endColumnIndex
* @param int $currentRow
* @param int $endRow
*/
private static function validateRange($cellBlock, $startColumnIndex, $endColumnIndex, $currentRow, $endRow): void
{
if ($startColumnIndex >= $endColumnIndex || $currentRow > $endRow) {
throw new Exception('Invalid range: "' . $cellBlock . '"');
}
}
}
How it Works

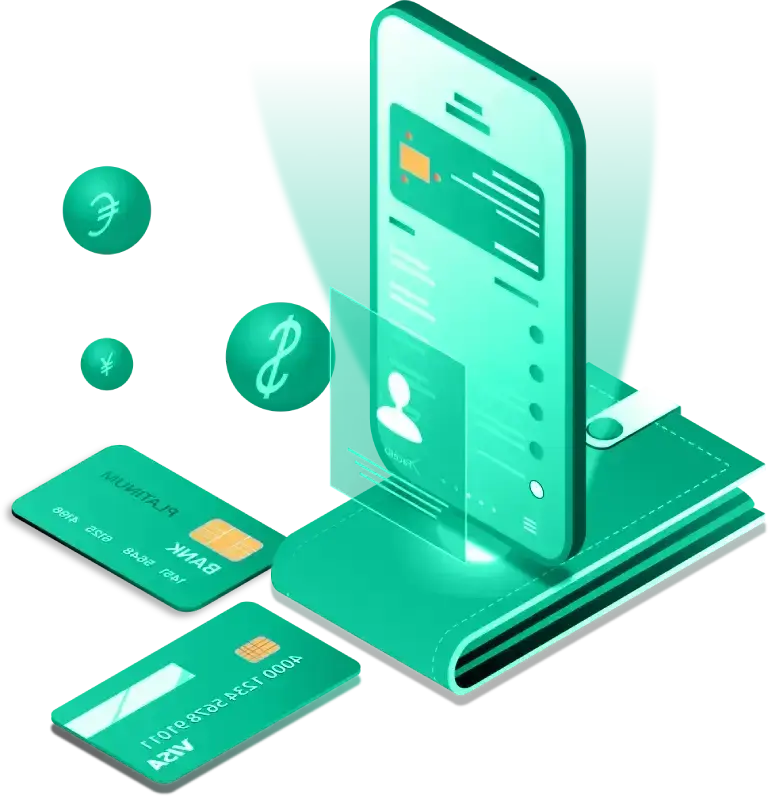
Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
