Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
/**
* League.Uri (https://uri.thephpleague.com)
*
* (c) Ignace Nyamagana Butera <nyamsprod@gmail.com>
*
* For the full copyright and license information, please view the LICENSE
* file that was distributed with this source code.
*/
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace League\Uri;
use League\Uri\Exceptions\IdnaConversionFailed;
use League\Uri\Exceptions\IdnSupportMissing;
use League\Uri\Exceptions\SyntaxError;
use League\Uri\Idna\Idna;
use TypeError;
use function array_merge;
use function explode;
use function filter_var;
use function gettype;
use function inet_pton;
use function is_object;
use function is_scalar;
use function method_exists;
use function preg_match;
use function rawurldecode;
use function sprintf;
use function strpos;
use function substr;
use const FILTER_FLAG_IPV6;
use const FILTER_VALIDATE_IP;
/**
* A class to parse a URI string according to RFC3986.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986
* @package League\Uri
* @author Ignace Nyamagana Butera <nyamsprod@gmail.com>
* @since 6.0.0
*/
final class UriString
{
/**
* Default URI component values.
*/
private const URI_COMPONENTS = [
'scheme' => null, 'user' => null, 'pass' => null, 'host' => null,
'port' => null, 'path' => '', 'query' => null, 'fragment' => null,
];
/**
* Simple URI which do not need any parsing.
*/
private const URI_SCHORTCUTS = [
'' => [],
'#' => ['fragment' => ''],
'?' => ['query' => ''],
'?#' => ['query' => '', 'fragment' => ''],
'/' => ['path' => '/'],
'//' => ['host' => ''],
];
/**
* Range of invalid characters in URI string.
*/
private const REGEXP_INVALID_URI_CHARS = '/[\x00-\x1f\x7f]/';
/**
* RFC3986 regular expression URI splitter.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#appendix-B
*/
private const REGEXP_URI_PARTS = ',^
(?<scheme>(?<scontent>[^:/?\#]+):)? # URI scheme component
(?<authority>//(?<acontent>[^/?\#]*))? # URI authority part
(?<path>[^?\#]*) # URI path component
(?<query>\?(?<qcontent>[^\#]*))? # URI query component
(?<fragment>\#(?<fcontent>.*))? # URI fragment component
,x';
/**
* URI scheme regular expresssion.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.1
*/
private const REGEXP_URI_SCHEME = '/^([a-z][a-z\d\+\.\-]*)?$/i';
/**
* IPvFuture regular expression.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
*/
private const REGEXP_IP_FUTURE = '/^
v(?<version>[A-F0-9])+\.
(?:
(?<unreserved>[a-z0-9_~\-\.])|
(?<sub_delims>[!$&\'()*+,;=:]) # also include the : character
)+
$/ix';
/**
* General registered name regular expression.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
*/
private const REGEXP_REGISTERED_NAME = '/(?(DEFINE)
(?<unreserved>[a-z0-9_~\-]) # . is missing as it is used to separate labels
(?<sub_delims>[!$&\'()*+,;=])
(?<encoded>%[A-F0-9]{2})
(?<reg_name>(?:(?&unreserved)|(?&sub_delims)|(?&encoded))*)
)
^(?:(?®_name)\.)*(?®_name)\.?$/ix';
/**
* Invalid characters in host regular expression.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
*/
private const REGEXP_INVALID_HOST_CHARS = '/
[:\/?#\[\]@ ] # gen-delims characters as well as the space character
/ix';
/**
* Invalid path for URI without scheme and authority regular expression.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.3
*/
private const REGEXP_INVALID_PATH = ',^(([^/]*):)(.*)?/,';
/**
* Host and Port splitter regular expression.
*/
private const REGEXP_HOST_PORT = ',^(?<host>\[.*\]|[^:]*)(:(?<port>.*))?$,';
/**
* IDN Host detector regular expression.
*/
private const REGEXP_IDN_PATTERN = '/[^\x20-\x7f]/';
/**
* Only the address block fe80::/10 can have a Zone ID attach to
* let's detect the link local significant 10 bits.
*/
private const ZONE_ID_ADDRESS_BLOCK = "\xfe\x80";
/**
* Generate an URI string representation from its parsed representation
* returned by League\UriString::parse() or PHP's parse_url.
*
* If you supply your own array, you are responsible for providing
* valid components without their URI delimiters.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-5.3
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-7.5
*
* @param array{
* scheme:?string,
* user:?string,
* pass:?string,
* host:?string,
* port:?int,
* path:?string,
* query:?string,
* fragment:?string
* } $components
*/
public static function build(array $components): string
{
$result = $components['path'] ?? '';
if (isset($components['query'])) {
$result .= '?'.$components['query'];
}
if (isset($components['fragment'])) {
$result .= '#'.$components['fragment'];
}
$scheme = null;
if (isset($components['scheme'])) {
$scheme = $components['scheme'].':';
}
if (!isset($components['host'])) {
return $scheme.$result;
}
$scheme .= '//';
$authority = $components['host'];
if (isset($components['port'])) {
$authority .= ':'.$components['port'];
}
if (!isset($components['user'])) {
return $scheme.$authority.$result;
}
$authority = '@'.$authority;
if (!isset($components['pass'])) {
return $scheme.$components['user'].$authority.$result;
}
return $scheme.$components['user'].':'.$components['pass'].$authority.$result;
}
/**
* Parse an URI string into its components.
*
* This method parses a URI and returns an associative array containing any
* of the various components of the URI that are present.
*
* <code>
* $components = (new Parser())->parse('http://foo@test.example.com:42?query#');
* var_export($components);
* //will display
* array(
* 'scheme' => 'http', // the URI scheme component
* 'user' => 'foo', // the URI user component
* 'pass' => null, // the URI pass component
* 'host' => 'test.example.com', // the URI host component
* 'port' => 42, // the URI port component
* 'path' => '', // the URI path component
* 'query' => 'query', // the URI query component
* 'fragment' => '', // the URI fragment component
* );
* </code>
*
* The returned array is similar to PHP's parse_url return value with the following
* differences:
*
* <ul>
* <li>All components are always present in the returned array</li>
* <li>Empty and undefined component are treated differently. And empty component is
* set to the empty string while an undefined component is set to the `null` value.</li>
* <li>The path component is never undefined</li>
* <li>The method parses the URI following the RFC3986 rules but you are still
* required to validate the returned components against its related scheme specific rules.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986
*
* @param mixed $uri any scalar or stringable object
*
* @throws SyntaxError if the URI contains invalid characters
* @throws SyntaxError if the URI contains an invalid scheme
* @throws SyntaxError if the URI contains an invalid path
*
* @return array{
* scheme:?string,
* user:?string,
* pass:?string,
* host:?string,
* port:?int,
* path:string,
* query:?string,
* fragment:?string
* }
*/
public static function parse($uri): array
{
if (is_object($uri) && method_exists($uri, '__toString')) {
$uri = (string) $uri;
}
if (!is_scalar($uri)) {
throw new TypeError(sprintf('The uri must be a scalar or a stringable object `%s` given', gettype($uri)));
}
$uri = (string) $uri;
if (isset(self::URI_SCHORTCUTS[$uri])) {
/** @var array{scheme:?string, user:?string, pass:?string, host:?string, port:?int, path:string, query:?string, fragment:?string} $components */
$components = array_merge(self::URI_COMPONENTS, self::URI_SCHORTCUTS[$uri]);
return $components;
}
if (1 === preg_match(self::REGEXP_INVALID_URI_CHARS, $uri)) {
throw new SyntaxError(sprintf('The uri `%s` contains invalid characters', $uri));
}
//if the first character is a known URI delimiter parsing can be simplified
$first_char = $uri[0];
//The URI is made of the fragment only
if ('#' === $first_char) {
[, $fragment] = explode('#', $uri, 2);
$components = self::URI_COMPONENTS;
$components['fragment'] = $fragment;
return $components;
}
//The URI is made of the query and fragment
if ('?' === $first_char) {
[, $partial] = explode('?', $uri, 2);
[$query, $fragment] = explode('#', $partial, 2) + [1 => null];
$components = self::URI_COMPONENTS;
$components['query'] = $query;
$components['fragment'] = $fragment;
return $components;
}
//use RFC3986 URI regexp to split the URI
preg_match(self::REGEXP_URI_PARTS, $uri, $parts);
$parts += ['query' => '', 'fragment' => ''];
if (':' === $parts['scheme'] || 1 !== preg_match(self::REGEXP_URI_SCHEME, $parts['scontent'])) {
throw new SyntaxError(sprintf('The uri `%s` contains an invalid scheme', $uri));
}
if ('' === $parts['scheme'].$parts['authority'] && 1 === preg_match(self::REGEXP_INVALID_PATH, $parts['path'])) {
throw new SyntaxError(sprintf('The uri `%s` contains an invalid path.', $uri));
}
/** @var array{scheme:?string, user:?string, pass:?string, host:?string, port:?int, path:string, query:?string, fragment:?string} $components */
$components = array_merge(
self::URI_COMPONENTS,
'' === $parts['authority'] ? [] : self::parseAuthority($parts['acontent']),
[
'path' => $parts['path'],
'scheme' => '' === $parts['scheme'] ? null : $parts['scontent'],
'query' => '' === $parts['query'] ? null : $parts['qcontent'],
'fragment' => '' === $parts['fragment'] ? null : $parts['fcontent'],
]
);
return $components;
}
/**
* Parses the URI authority part.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2
*
* @throws SyntaxError If the port component is invalid
*
* @return array{user:?string, pass:?string, host:?string, port:?int}
*/
private static function parseAuthority(string $authority): array
{
$components = ['user' => null, 'pass' => null, 'host' => '', 'port' => null];
if ('' === $authority) {
return $components;
}
$parts = explode('@', $authority, 2);
if (isset($parts[1])) {
[$components['user'], $components['pass']] = explode(':', $parts[0], 2) + [1 => null];
}
preg_match(self::REGEXP_HOST_PORT, $parts[1] ?? $parts[0], $matches);
$matches += ['port' => ''];
$components['port'] = self::filterPort($matches['port']);
$components['host'] = self::filterHost($matches['host']);
return $components;
}
/**
* Filter and format the port component.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
*
* @throws SyntaxError if the registered name is invalid
*/
private static function filterPort(string $port): ?int
{
if ('' === $port) {
return null;
}
if (1 === preg_match('/^\d*$/', $port)) {
return (int) $port;
}
throw new SyntaxError(sprintf('The port `%s` is invalid', $port));
}
/**
* Returns whether a hostname is valid.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
*
* @throws SyntaxError if the registered name is invalid
*/
private static function filterHost(string $host): string
{
if ('' === $host) {
return $host;
}
if ('[' !== $host[0] || ']' !== substr($host, -1)) {
return self::filterRegisteredName($host);
}
if (!self::isIpHost(substr($host, 1, -1))) {
throw new SyntaxError(sprintf('Host `%s` is invalid : the IP host is malformed', $host));
}
return $host;
}
/**
* Returns whether the host is an IPv4 or a registered named.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
*
* @throws SyntaxError if the registered name is invalid
* @throws IdnSupportMissing if IDN support or ICU requirement are not available or met.
*/
private static function filterRegisteredName(string $host): string
{
$formatted_host = rawurldecode($host);
if (1 === preg_match(self::REGEXP_REGISTERED_NAME, $formatted_host)) {
return $host;
}
//to test IDN host non-ascii characters must be present in the host
if (1 !== preg_match(self::REGEXP_IDN_PATTERN, $formatted_host)) {
throw new SyntaxError(sprintf('Host `%s` is invalid : the host is not a valid registered name', $host));
}
$info = Idna::toAscii($host, Idna::IDNA2008_ASCII);
if (0 !== $info->errors()) {
throw IdnaConversionFailed::dueToIDNAError($host, $info);
}
return $host;
}
/**
* Validates a IPv6/IPvfuture host.
*
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#section-3.2.2
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6874#section-2
* @link https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6874#section-4
*/
private static function isIpHost(string $ip_host): bool
{
if (false !== filter_var($ip_host, FILTER_VALIDATE_IP, FILTER_FLAG_IPV6)) {
return true;
}
if (1 === preg_match(self::REGEXP_IP_FUTURE, $ip_host, $matches)) {
return !in_array($matches['version'], ['4', '6'], true);
}
$pos = strpos($ip_host, '%');
if (false === $pos || 1 === preg_match(
self::REGEXP_INVALID_HOST_CHARS,
rawurldecode(substr($ip_host, $pos))
)) {
return false;
}
$ip_host = substr($ip_host, 0, $pos);
return false !== filter_var($ip_host, FILTER_VALIDATE_IP, FILTER_FLAG_IPV6)
&& 0 === strpos((string) inet_pton($ip_host), self::ZONE_ID_ADDRESS_BLOCK);
}
}
How it Works

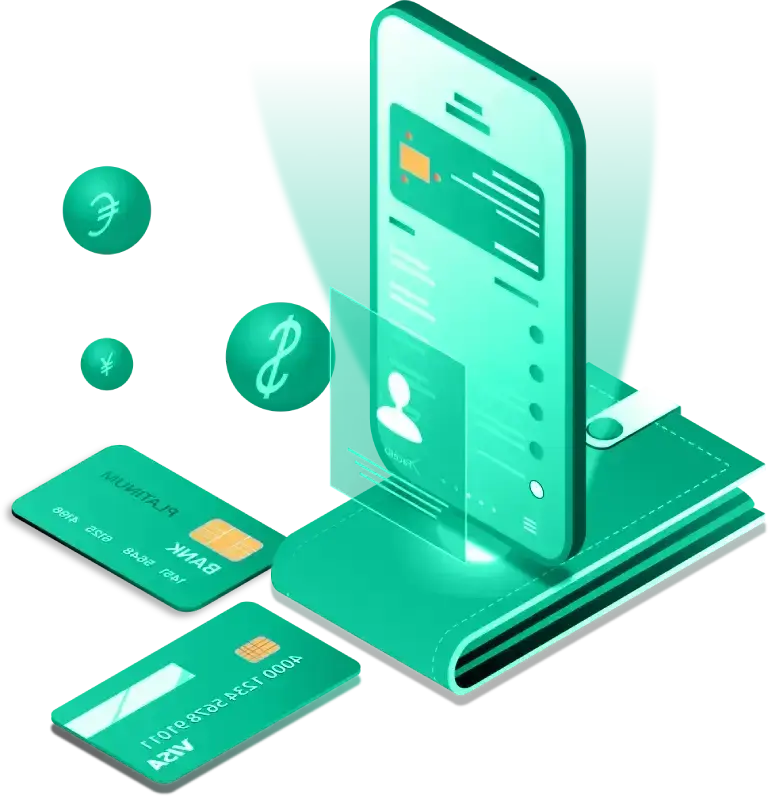
Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
