Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace GuzzleHttp\Psr7;
use Psr\Http\Message\UriInterface;
/**
* Provides methods to normalize and compare URIs.
*
* @author Tobias Schultze
*
* @see https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3986#section-6
*/
final class UriNormalizer
{
/**
* Default normalizations which only include the ones that preserve semantics.
*/
public const PRESERVING_NORMALIZATIONS =
self::CAPITALIZE_PERCENT_ENCODING |
self::DECODE_UNRESERVED_CHARACTERS |
self::CONVERT_EMPTY_PATH |
self::REMOVE_DEFAULT_HOST |
self::REMOVE_DEFAULT_PORT |
self::REMOVE_DOT_SEGMENTS;
/**
* All letters within a percent-encoding triplet (e.g., "%3A") are case-insensitive, and should be capitalized.
*
* Example: http://example.org/a%c2%b1b → http://example.org/a%C2%B1b
*/
public const CAPITALIZE_PERCENT_ENCODING = 1;
/**
* Decodes percent-encoded octets of unreserved characters.
*
* For consistency, percent-encoded octets in the ranges of ALPHA (%41–%5A and %61–%7A), DIGIT (%30–%39),
* hyphen (%2D), period (%2E), underscore (%5F), or tilde (%7E) should not be created by URI producers and,
* when found in a URI, should be decoded to their corresponding unreserved characters by URI normalizers.
*
* Example: http://example.org/%7Eusern%61me/ → http://example.org/~username/
*/
public const DECODE_UNRESERVED_CHARACTERS = 2;
/**
* Converts the empty path to "/" for http and https URIs.
*
* Example: http://example.org → http://example.org/
*/
public const CONVERT_EMPTY_PATH = 4;
/**
* Removes the default host of the given URI scheme from the URI.
*
* Only the "file" scheme defines the default host "localhost".
* All of `file:/myfile`, `file:///myfile`, and `file://localhost/myfile`
* are equivalent according to RFC 3986. The first format is not accepted
* by PHPs stream functions and thus already normalized implicitly to the
* second format in the Uri class. See `GuzzleHttp\Psr7\Uri::composeComponents`.
*
* Example: file://localhost/myfile → file:///myfile
*/
public const REMOVE_DEFAULT_HOST = 8;
/**
* Removes the default port of the given URI scheme from the URI.
*
* Example: http://example.org:80/ → http://example.org/
*/
public const REMOVE_DEFAULT_PORT = 16;
/**
* Removes unnecessary dot-segments.
*
* Dot-segments in relative-path references are not removed as it would
* change the semantics of the URI reference.
*
* Example: http://example.org/../a/b/../c/./d.html → http://example.org/a/c/d.html
*/
public const REMOVE_DOT_SEGMENTS = 32;
/**
* Paths which include two or more adjacent slashes are converted to one.
*
* Webservers usually ignore duplicate slashes and treat those URIs equivalent.
* But in theory those URIs do not need to be equivalent. So this normalization
* may change the semantics. Encoded slashes (%2F) are not removed.
*
* Example: http://example.org//foo///bar.html → http://example.org/foo/bar.html
*/
public const REMOVE_DUPLICATE_SLASHES = 64;
/**
* Sort query parameters with their values in alphabetical order.
*
* However, the order of parameters in a URI may be significant (this is not defined by the standard).
* So this normalization is not safe and may change the semantics of the URI.
*
* Example: ?lang=en&article=fred → ?article=fred&lang=en
*
* Note: The sorting is neither locale nor Unicode aware (the URI query does not get decoded at all) as the
* purpose is to be able to compare URIs in a reproducible way, not to have the params sorted perfectly.
*/
public const SORT_QUERY_PARAMETERS = 128;
/**
* Returns a normalized URI.
*
* The scheme and host component are already normalized to lowercase per PSR-7 UriInterface.
* This methods adds additional normalizations that can be configured with the $flags parameter.
*
* PSR-7 UriInterface cannot distinguish between an empty component and a missing component as
* getQuery(), getFragment() etc. always return a string. This means the URIs "/?#" and "/" are
* treated equivalent which is not necessarily true according to RFC 3986. But that difference
* is highly uncommon in reality. So this potential normalization is implied in PSR-7 as well.
*
* @param UriInterface $uri The URI to normalize
* @param int $flags A bitmask of normalizations to apply, see constants
*
* @see https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3986#section-6.2
*/
public static function normalize(UriInterface $uri, int $flags = self::PRESERVING_NORMALIZATIONS): UriInterface
{
if ($flags & self::CAPITALIZE_PERCENT_ENCODING) {
$uri = self::capitalizePercentEncoding($uri);
}
if ($flags & self::DECODE_UNRESERVED_CHARACTERS) {
$uri = self::decodeUnreservedCharacters($uri);
}
if ($flags & self::CONVERT_EMPTY_PATH && $uri->getPath() === ''
&& ($uri->getScheme() === 'http' || $uri->getScheme() === 'https')
) {
$uri = $uri->withPath('/');
}
if ($flags & self::REMOVE_DEFAULT_HOST && $uri->getScheme() === 'file' && $uri->getHost() === 'localhost') {
$uri = $uri->withHost('');
}
if ($flags & self::REMOVE_DEFAULT_PORT && $uri->getPort() !== null && Uri::isDefaultPort($uri)) {
$uri = $uri->withPort(null);
}
if ($flags & self::REMOVE_DOT_SEGMENTS && !Uri::isRelativePathReference($uri)) {
$uri = $uri->withPath(UriResolver::removeDotSegments($uri->getPath()));
}
if ($flags & self::REMOVE_DUPLICATE_SLASHES) {
$uri = $uri->withPath(preg_replace('#//++#', '/', $uri->getPath()));
}
if ($flags & self::SORT_QUERY_PARAMETERS && $uri->getQuery() !== '') {
$queryKeyValues = explode('&', $uri->getQuery());
sort($queryKeyValues);
$uri = $uri->withQuery(implode('&', $queryKeyValues));
}
return $uri;
}
/**
* Whether two URIs can be considered equivalent.
*
* Both URIs are normalized automatically before comparison with the given $normalizations bitmask. The method also
* accepts relative URI references and returns true when they are equivalent. This of course assumes they will be
* resolved against the same base URI. If this is not the case, determination of equivalence or difference of
* relative references does not mean anything.
*
* @param UriInterface $uri1 An URI to compare
* @param UriInterface $uri2 An URI to compare
* @param int $normalizations A bitmask of normalizations to apply, see constants
*
* @see https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3986#section-6.1
*/
public static function isEquivalent(UriInterface $uri1, UriInterface $uri2, int $normalizations = self::PRESERVING_NORMALIZATIONS): bool
{
return (string) self::normalize($uri1, $normalizations) === (string) self::normalize($uri2, $normalizations);
}
private static function capitalizePercentEncoding(UriInterface $uri): UriInterface
{
$regex = '/(?:%[A-Fa-f0-9]{2})++/';
$callback = function (array $match): string {
return strtoupper($match[0]);
};
return
$uri->withPath(
preg_replace_callback($regex, $callback, $uri->getPath())
)->withQuery(
preg_replace_callback($regex, $callback, $uri->getQuery())
);
}
private static function decodeUnreservedCharacters(UriInterface $uri): UriInterface
{
$regex = '/%(?:2D|2E|5F|7E|3[0-9]|[46][1-9A-F]|[57][0-9A])/i';
$callback = function (array $match): string {
return rawurldecode($match[0]);
};
return
$uri->withPath(
preg_replace_callback($regex, $callback, $uri->getPath())
)->withQuery(
preg_replace_callback($regex, $callback, $uri->getQuery())
);
}
private function __construct()
{
// cannot be instantiated
}
}
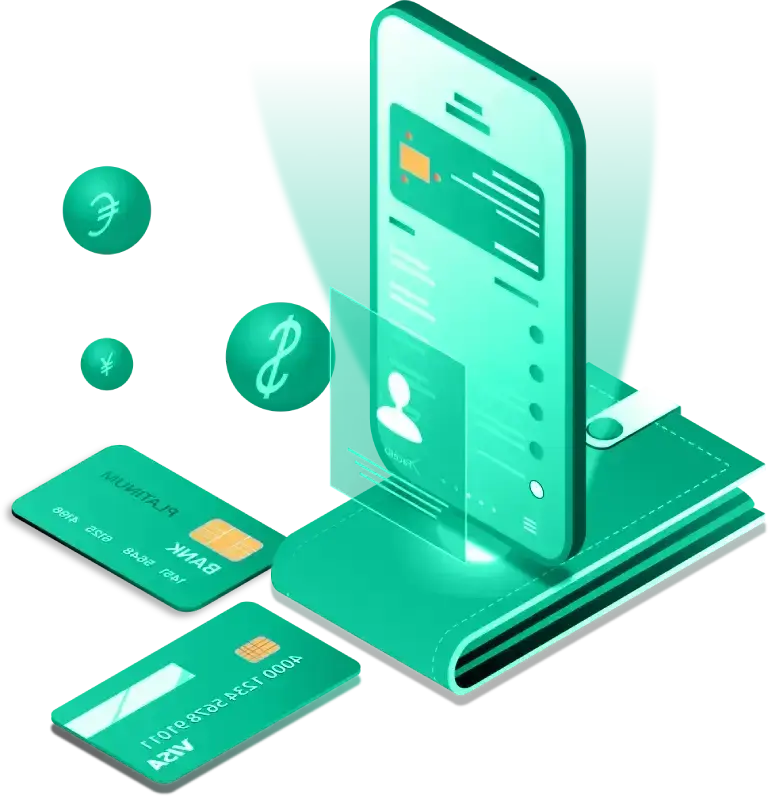
How it Works

Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
