Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace Brick\Math;
use Brick\Math\Exception\DivisionByZeroException;
use Brick\Math\Exception\IntegerOverflowException;
use Brick\Math\Exception\MathException;
use Brick\Math\Exception\NegativeNumberException;
use Brick\Math\Exception\NumberFormatException;
use Brick\Math\Internal\Calculator;
/**
* An arbitrary-size integer.
*
* All methods accepting a number as a parameter accept either a BigInteger instance,
* an integer, or a string representing an arbitrary size integer.
*
* @psalm-immutable
*/
final class BigInteger extends BigNumber
{
/**
* The value, as a string of digits with optional leading minus sign.
*
* No leading zeros must be present.
* No leading minus sign must be present if the number is zero.
*/
private string $value;
/**
* Protected constructor. Use a factory method to obtain an instance.
*
* @param string $value A string of digits, with optional leading minus sign.
*/
protected function __construct(string $value)
{
$this->value = $value;
}
/**
* Creates a BigInteger of the given value.
*
* @throws MathException If the value cannot be converted to a BigInteger.
*
* @psalm-pure
*/
public static function of(BigNumber|int|float|string $value) : BigInteger
{
return parent::of($value)->toBigInteger();
}
/**
* Creates a number from a string in a given base.
*
* The string can optionally be prefixed with the `+` or `-` sign.
*
* Bases greater than 36 are not supported by this method, as there is no clear consensus on which of the lowercase
* or uppercase characters should come first. Instead, this method accepts any base up to 36, and does not
* differentiate lowercase and uppercase characters, which are considered equal.
*
* For bases greater than 36, and/or custom alphabets, use the fromArbitraryBase() method.
*
* @param string $number The number to convert, in the given base.
* @param int $base The base of the number, between 2 and 36.
*
* @throws NumberFormatException If the number is empty, or contains invalid chars for the given base.
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If the base is out of range.
*
* @psalm-pure
*/
public static function fromBase(string $number, int $base) : BigInteger
{
if ($number === '') {
throw new NumberFormatException('The number cannot be empty.');
}
if ($base < 2 || $base > 36) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException(\sprintf('Base %d is not in range 2 to 36.', $base));
}
if ($number[0] === '-') {
$sign = '-';
$number = \substr($number, 1);
} elseif ($number[0] === '+') {
$sign = '';
$number = \substr($number, 1);
} else {
$sign = '';
}
if ($number === '') {
throw new NumberFormatException('The number cannot be empty.');
}
$number = \ltrim($number, '0');
if ($number === '') {
// The result will be the same in any base, avoid further calculation.
return BigInteger::zero();
}
if ($number === '1') {
// The result will be the same in any base, avoid further calculation.
return new BigInteger($sign . '1');
}
$pattern = '/[^' . \substr(Calculator::ALPHABET, 0, $base) . ']/';
if (\preg_match($pattern, \strtolower($number), $matches) === 1) {
throw new NumberFormatException(\sprintf('"%s" is not a valid character in base %d.', $matches[0], $base));
}
if ($base === 10) {
// The number is usable as is, avoid further calculation.
return new BigInteger($sign . $number);
}
$result = Calculator::get()->fromBase($number, $base);
return new BigInteger($sign . $result);
}
/**
* Parses a string containing an integer in an arbitrary base, using a custom alphabet.
*
* Because this method accepts an alphabet with any character, including dash, it does not handle negative numbers.
*
* @param string $number The number to parse.
* @param string $alphabet The alphabet, for example '01' for base 2, or '01234567' for base 8.
*
* @throws NumberFormatException If the given number is empty or contains invalid chars for the given alphabet.
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If the alphabet does not contain at least 2 chars.
*
* @psalm-pure
*/
public static function fromArbitraryBase(string $number, string $alphabet) : BigInteger
{
if ($number === '') {
throw new NumberFormatException('The number cannot be empty.');
}
$base = \strlen($alphabet);
if ($base < 2) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('The alphabet must contain at least 2 chars.');
}
$pattern = '/[^' . \preg_quote($alphabet, '/') . ']/';
if (\preg_match($pattern, $number, $matches) === 1) {
throw NumberFormatException::charNotInAlphabet($matches[0]);
}
$number = Calculator::get()->fromArbitraryBase($number, $alphabet, $base);
return new BigInteger($number);
}
/**
* Translates a string of bytes containing the binary representation of a BigInteger into a BigInteger.
*
* The input string is assumed to be in big-endian byte-order: the most significant byte is in the zeroth element.
*
* If `$signed` is true, the input is assumed to be in two's-complement representation, and the leading bit is
* interpreted as a sign bit. If `$signed` is false, the input is interpreted as an unsigned number, and the
* resulting BigInteger will always be positive or zero.
*
* This method can be used to retrieve a number exported by `toBytes()`, as long as the `$signed` flags match.
*
* @param string $value The byte string.
* @param bool $signed Whether to interpret as a signed number in two's-complement representation with a leading
* sign bit.
*
* @throws NumberFormatException If the string is empty.
*/
public static function fromBytes(string $value, bool $signed = true) : BigInteger
{
if ($value === '') {
throw new NumberFormatException('The byte string must not be empty.');
}
$twosComplement = false;
if ($signed) {
$x = \ord($value[0]);
if (($twosComplement = ($x >= 0x80))) {
$value = ~$value;
}
}
$number = self::fromBase(\bin2hex($value), 16);
if ($twosComplement) {
return $number->plus(1)->negated();
}
return $number;
}
/**
* Generates a pseudo-random number in the range 0 to 2^numBits - 1.
*
* Using the default random bytes generator, this method is suitable for cryptographic use.
*
* @psalm-param (callable(int): string)|null $randomBytesGenerator
*
* @param int $numBits The number of bits.
* @param callable|null $randomBytesGenerator A function that accepts a number of bytes as an integer, and returns a
* string of random bytes of the given length. Defaults to the
* `random_bytes()` function.
*
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If $numBits is negative.
*/
public static function randomBits(int $numBits, ?callable $randomBytesGenerator = null) : BigInteger
{
if ($numBits < 0) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('The number of bits cannot be negative.');
}
if ($numBits === 0) {
return BigInteger::zero();
}
if ($randomBytesGenerator === null) {
$randomBytesGenerator = 'random_bytes';
}
$byteLength = \intdiv($numBits - 1, 8) + 1;
$extraBits = ($byteLength * 8 - $numBits);
$bitmask = \chr(0xFF >> $extraBits);
$randomBytes = $randomBytesGenerator($byteLength);
$randomBytes[0] = $randomBytes[0] & $bitmask;
return self::fromBytes($randomBytes, false);
}
/**
* Generates a pseudo-random number between `$min` and `$max`.
*
* Using the default random bytes generator, this method is suitable for cryptographic use.
*
* @psalm-param (callable(int): string)|null $randomBytesGenerator
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $min The lower bound. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $max The upper bound. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
* @param callable|null $randomBytesGenerator A function that accepts a number of bytes as an integer,
* and returns a string of random bytes of the given length.
* Defaults to the `random_bytes()` function.
*
* @throws MathException If one of the parameters cannot be converted to a BigInteger,
* or `$min` is greater than `$max`.
*/
public static function randomRange(
BigNumber|int|float|string $min,
BigNumber|int|float|string $max,
?callable $randomBytesGenerator = null
) : BigInteger {
$min = BigInteger::of($min);
$max = BigInteger::of($max);
if ($min->isGreaterThan($max)) {
throw new MathException('$min cannot be greater than $max.');
}
if ($min->isEqualTo($max)) {
return $min;
}
$diff = $max->minus($min);
$bitLength = $diff->getBitLength();
// try until the number is in range (50% to 100% chance of success)
do {
$randomNumber = self::randomBits($bitLength, $randomBytesGenerator);
} while ($randomNumber->isGreaterThan($diff));
return $randomNumber->plus($min);
}
/**
* Returns a BigInteger representing zero.
*
* @psalm-pure
*/
public static function zero() : BigInteger
{
/**
* @psalm-suppress ImpureStaticVariable
* @var BigInteger|null $zero
*/
static $zero;
if ($zero === null) {
$zero = new BigInteger('0');
}
return $zero;
}
/**
* Returns a BigInteger representing one.
*
* @psalm-pure
*/
public static function one() : BigInteger
{
/**
* @psalm-suppress ImpureStaticVariable
* @var BigInteger|null $one
*/
static $one;
if ($one === null) {
$one = new BigInteger('1');
}
return $one;
}
/**
* Returns a BigInteger representing ten.
*
* @psalm-pure
*/
public static function ten() : BigInteger
{
/**
* @psalm-suppress ImpureStaticVariable
* @var BigInteger|null $ten
*/
static $ten;
if ($ten === null) {
$ten = new BigInteger('10');
}
return $ten;
}
public static function gcdMultiple(BigInteger $a, BigInteger ...$n): BigInteger
{
$result = $a;
foreach ($n as $next) {
$result = $result->gcd($next);
if ($result->isEqualTo(1)) {
return $result;
}
}
return $result;
}
/**
* Returns the sum of this number and the given one.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The number to add. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @throws MathException If the number is not valid, or is not convertible to a BigInteger.
*/
public function plus(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '0') {
return $this;
}
if ($this->value === '0') {
return $that;
}
$value = Calculator::get()->add($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns the difference of this number and the given one.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The number to subtract. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @throws MathException If the number is not valid, or is not convertible to a BigInteger.
*/
public function minus(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '0') {
return $this;
}
$value = Calculator::get()->sub($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns the product of this number and the given one.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The multiplier. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @throws MathException If the multiplier is not a valid number, or is not convertible to a BigInteger.
*/
public function multipliedBy(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '1') {
return $this;
}
if ($this->value === '1') {
return $that;
}
$value = Calculator::get()->mul($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns the result of the division of this number by the given one.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The divisor. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
* @param int $roundingMode An optional rounding mode.
*
* @throws MathException If the divisor is not a valid number, is not convertible to a BigInteger, is zero,
* or RoundingMode::UNNECESSARY is used and the remainder is not zero.
*/
public function dividedBy(BigNumber|int|float|string $that, int $roundingMode = RoundingMode::UNNECESSARY) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '1') {
return $this;
}
if ($that->value === '0') {
throw DivisionByZeroException::divisionByZero();
}
$result = Calculator::get()->divRound($this->value, $that->value, $roundingMode);
return new BigInteger($result);
}
/**
* Returns this number exponentiated to the given value.
*
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If the exponent is not in the range 0 to 1,000,000.
*/
public function power(int $exponent) : BigInteger
{
if ($exponent === 0) {
return BigInteger::one();
}
if ($exponent === 1) {
return $this;
}
if ($exponent < 0 || $exponent > Calculator::MAX_POWER) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException(\sprintf(
'The exponent %d is not in the range 0 to %d.',
$exponent,
Calculator::MAX_POWER
));
}
return new BigInteger(Calculator::get()->pow($this->value, $exponent));
}
/**
* Returns the quotient of the division of this number by the given one.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The divisor. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @throws DivisionByZeroException If the divisor is zero.
*/
public function quotient(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '1') {
return $this;
}
if ($that->value === '0') {
throw DivisionByZeroException::divisionByZero();
}
$quotient = Calculator::get()->divQ($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($quotient);
}
/**
* Returns the remainder of the division of this number by the given one.
*
* The remainder, when non-zero, has the same sign as the dividend.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The divisor. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @throws DivisionByZeroException If the divisor is zero.
*/
public function remainder(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '1') {
return BigInteger::zero();
}
if ($that->value === '0') {
throw DivisionByZeroException::divisionByZero();
}
$remainder = Calculator::get()->divR($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($remainder);
}
/**
* Returns the quotient and remainder of the division of this number by the given one.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The divisor. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @return BigInteger[] An array containing the quotient and the remainder.
*
* @throws DivisionByZeroException If the divisor is zero.
*/
public function quotientAndRemainder(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : array
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '0') {
throw DivisionByZeroException::divisionByZero();
}
[$quotient, $remainder] = Calculator::get()->divQR($this->value, $that->value);
return [
new BigInteger($quotient),
new BigInteger($remainder)
];
}
/**
* Returns the modulo of this number and the given one.
*
* The modulo operation yields the same result as the remainder operation when both operands are of the same sign,
* and may differ when signs are different.
*
* The result of the modulo operation, when non-zero, has the same sign as the divisor.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The divisor. Must be convertible to a BigInteger.
*
* @throws DivisionByZeroException If the divisor is zero.
*/
public function mod(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '0') {
throw DivisionByZeroException::modulusMustNotBeZero();
}
$value = Calculator::get()->mod($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns the modular multiplicative inverse of this BigInteger modulo $m.
*
* @throws DivisionByZeroException If $m is zero.
* @throws NegativeNumberException If $m is negative.
* @throws MathException If this BigInteger has no multiplicative inverse mod m (that is, this BigInteger
* is not relatively prime to m).
*/
public function modInverse(BigInteger $m) : BigInteger
{
if ($m->value === '0') {
throw DivisionByZeroException::modulusMustNotBeZero();
}
if ($m->isNegative()) {
throw new NegativeNumberException('Modulus must not be negative.');
}
if ($m->value === '1') {
return BigInteger::zero();
}
$value = Calculator::get()->modInverse($this->value, $m->value);
if ($value === null) {
throw new MathException('Unable to compute the modInverse for the given modulus.');
}
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns this number raised into power with modulo.
*
* This operation only works on positive numbers.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $exp The exponent. Must be positive or zero.
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $mod The modulus. Must be strictly positive.
*
* @throws NegativeNumberException If any of the operands is negative.
* @throws DivisionByZeroException If the modulus is zero.
*/
public function modPow(BigNumber|int|float|string $exp, BigNumber|int|float|string $mod) : BigInteger
{
$exp = BigInteger::of($exp);
$mod = BigInteger::of($mod);
if ($this->isNegative() || $exp->isNegative() || $mod->isNegative()) {
throw new NegativeNumberException('The operands cannot be negative.');
}
if ($mod->isZero()) {
throw DivisionByZeroException::modulusMustNotBeZero();
}
$result = Calculator::get()->modPow($this->value, $exp->value, $mod->value);
return new BigInteger($result);
}
/**
* Returns the greatest common divisor of this number and the given one.
*
* The GCD is always positive, unless both operands are zero, in which case it is zero.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The operand. Must be convertible to an integer number.
*/
public function gcd(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
if ($that->value === '0' && $this->value[0] !== '-') {
return $this;
}
if ($this->value === '0' && $that->value[0] !== '-') {
return $that;
}
$value = Calculator::get()->gcd($this->value, $that->value);
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns the integer square root number of this number, rounded down.
*
* The result is the largest x such that x² ≤ n.
*
* @throws NegativeNumberException If this number is negative.
*/
public function sqrt() : BigInteger
{
if ($this->value[0] === '-') {
throw new NegativeNumberException('Cannot calculate the square root of a negative number.');
}
$value = Calculator::get()->sqrt($this->value);
return new BigInteger($value);
}
/**
* Returns the absolute value of this number.
*/
public function abs() : BigInteger
{
return $this->isNegative() ? $this->negated() : $this;
}
/**
* Returns the inverse of this number.
*/
public function negated() : BigInteger
{
return new BigInteger(Calculator::get()->neg($this->value));
}
/**
* Returns the integer bitwise-and combined with another integer.
*
* This method returns a negative BigInteger if and only if both operands are negative.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The operand. Must be convertible to an integer number.
*/
public function and(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
return new BigInteger(Calculator::get()->and($this->value, $that->value));
}
/**
* Returns the integer bitwise-or combined with another integer.
*
* This method returns a negative BigInteger if and only if either of the operands is negative.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The operand. Must be convertible to an integer number.
*/
public function or(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
return new BigInteger(Calculator::get()->or($this->value, $that->value));
}
/**
* Returns the integer bitwise-xor combined with another integer.
*
* This method returns a negative BigInteger if and only if exactly one of the operands is negative.
*
* @param BigNumber|int|float|string $that The operand. Must be convertible to an integer number.
*/
public function xor(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : BigInteger
{
$that = BigInteger::of($that);
return new BigInteger(Calculator::get()->xor($this->value, $that->value));
}
/**
* Returns the bitwise-not of this BigInteger.
*/
public function not() : BigInteger
{
return $this->negated()->minus(1);
}
/**
* Returns the integer left shifted by a given number of bits.
*/
public function shiftedLeft(int $distance) : BigInteger
{
if ($distance === 0) {
return $this;
}
if ($distance < 0) {
return $this->shiftedRight(- $distance);
}
return $this->multipliedBy(BigInteger::of(2)->power($distance));
}
/**
* Returns the integer right shifted by a given number of bits.
*/
public function shiftedRight(int $distance) : BigInteger
{
if ($distance === 0) {
return $this;
}
if ($distance < 0) {
return $this->shiftedLeft(- $distance);
}
$operand = BigInteger::of(2)->power($distance);
if ($this->isPositiveOrZero()) {
return $this->quotient($operand);
}
return $this->dividedBy($operand, RoundingMode::UP);
}
/**
* Returns the number of bits in the minimal two's-complement representation of this BigInteger, excluding a sign bit.
*
* For positive BigIntegers, this is equivalent to the number of bits in the ordinary binary representation.
* Computes (ceil(log2(this < 0 ? -this : this+1))).
*/
public function getBitLength() : int
{
if ($this->value === '0') {
return 0;
}
if ($this->isNegative()) {
return $this->abs()->minus(1)->getBitLength();
}
return \strlen($this->toBase(2));
}
/**
* Returns the index of the rightmost (lowest-order) one bit in this BigInteger.
*
* Returns -1 if this BigInteger contains no one bits.
*/
public function getLowestSetBit() : int
{
$n = $this;
$bitLength = $this->getBitLength();
for ($i = 0; $i <= $bitLength; $i++) {
if ($n->isOdd()) {
return $i;
}
$n = $n->shiftedRight(1);
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns whether this number is even.
*/
public function isEven() : bool
{
return \in_array($this->value[-1], ['0', '2', '4', '6', '8'], true);
}
/**
* Returns whether this number is odd.
*/
public function isOdd() : bool
{
return \in_array($this->value[-1], ['1', '3', '5', '7', '9'], true);
}
/**
* Returns true if and only if the designated bit is set.
*
* Computes ((this & (1<<n)) != 0).
*
* @param int $n The bit to test, 0-based.
*
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If the bit to test is negative.
*/
public function testBit(int $n) : bool
{
if ($n < 0) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('The bit to test cannot be negative.');
}
return $this->shiftedRight($n)->isOdd();
}
public function compareTo(BigNumber|int|float|string $that) : int
{
$that = BigNumber::of($that);
if ($that instanceof BigInteger) {
return Calculator::get()->cmp($this->value, $that->value);
}
return - $that->compareTo($this);
}
public function getSign() : int
{
return ($this->value === '0') ? 0 : (($this->value[0] === '-') ? -1 : 1);
}
public function toBigInteger() : BigInteger
{
return $this;
}
public function toBigDecimal() : BigDecimal
{
return self::newBigDecimal($this->value);
}
public function toBigRational() : BigRational
{
return self::newBigRational($this, BigInteger::one(), false);
}
public function toScale(int $scale, int $roundingMode = RoundingMode::UNNECESSARY) : BigDecimal
{
return $this->toBigDecimal()->toScale($scale, $roundingMode);
}
public function toInt() : int
{
$intValue = (int) $this->value;
if ($this->value !== (string) $intValue) {
throw IntegerOverflowException::toIntOverflow($this);
}
return $intValue;
}
public function toFloat() : float
{
return (float) $this->value;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this number in the given base.
*
* The output will always be lowercase for bases greater than 10.
*
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If the base is out of range.
*/
public function toBase(int $base) : string
{
if ($base === 10) {
return $this->value;
}
if ($base < 2 || $base > 36) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException(\sprintf('Base %d is out of range [2, 36]', $base));
}
return Calculator::get()->toBase($this->value, $base);
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this number in an arbitrary base with a custom alphabet.
*
* Because this method accepts an alphabet with any character, including dash, it does not handle negative numbers;
* a NegativeNumberException will be thrown when attempting to call this method on a negative number.
*
* @param string $alphabet The alphabet, for example '01' for base 2, or '01234567' for base 8.
*
* @throws NegativeNumberException If this number is negative.
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException If the given alphabet does not contain at least 2 chars.
*/
public function toArbitraryBase(string $alphabet) : string
{
$base = \strlen($alphabet);
if ($base < 2) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('The alphabet must contain at least 2 chars.');
}
if ($this->value[0] === '-') {
throw new NegativeNumberException(__FUNCTION__ . '() does not support negative numbers.');
}
return Calculator::get()->toArbitraryBase($this->value, $alphabet, $base);
}
/**
* Returns a string of bytes containing the binary representation of this BigInteger.
*
* The string is in big-endian byte-order: the most significant byte is in the zeroth element.
*
* If `$signed` is true, the output will be in two's-complement representation, and a sign bit will be prepended to
* the output. If `$signed` is false, no sign bit will be prepended, and this method will throw an exception if the
* number is negative.
*
* The string will contain the minimum number of bytes required to represent this BigInteger, including a sign bit
* if `$signed` is true.
*
* This representation is compatible with the `fromBytes()` factory method, as long as the `$signed` flags match.
*
* @param bool $signed Whether to output a signed number in two's-complement representation with a leading sign bit.
*
* @throws NegativeNumberException If $signed is false, and the number is negative.
*/
public function toBytes(bool $signed = true) : string
{
if (! $signed && $this->isNegative()) {
throw new NegativeNumberException('Cannot convert a negative number to a byte string when $signed is false.');
}
$hex = $this->abs()->toBase(16);
if (\strlen($hex) % 2 !== 0) {
$hex = '0' . $hex;
}
$baseHexLength = \strlen($hex);
if ($signed) {
if ($this->isNegative()) {
$bin = \hex2bin($hex);
assert($bin !== false);
$hex = \bin2hex(~$bin);
$hex = self::fromBase($hex, 16)->plus(1)->toBase(16);
$hexLength = \strlen($hex);
if ($hexLength < $baseHexLength) {
$hex = \str_repeat('0', $baseHexLength - $hexLength) . $hex;
}
if ($hex[0] < '8') {
$hex = 'FF' . $hex;
}
} else {
if ($hex[0] >= '8') {
$hex = '00' . $hex;
}
}
}
return \hex2bin($hex);
}
public function __toString() : string
{
return $this->value;
}
/**
* This method is required for serializing the object and SHOULD NOT be accessed directly.
*
* @internal
*
* @return array{value: string}
*/
public function __serialize(): array
{
return ['value' => $this->value];
}
/**
* This method is only here to allow unserializing the object and cannot be accessed directly.
*
* @internal
* @psalm-suppress RedundantPropertyInitializationCheck
*
* @param array{value: string} $data
*
* @throws \LogicException
*/
public function __unserialize(array $data): void
{
if (isset($this->value)) {
throw new \LogicException('__unserialize() is an internal function, it must not be called directly.');
}
$this->value = $data['value'];
}
/**
* This method is required by interface Serializable and SHOULD NOT be accessed directly.
*
* @internal
*/
public function serialize() : string
{
return $this->value;
}
/**
* This method is only here to implement interface Serializable and cannot be accessed directly.
*
* @internal
* @psalm-suppress RedundantPropertyInitializationCheck
*
* @throws \LogicException
*/
public function unserialize($value) : void
{
if (isset($this->value)) {
throw new \LogicException('unserialize() is an internal function, it must not be called directly.');
}
$this->value = $value;
}
}
How it Works

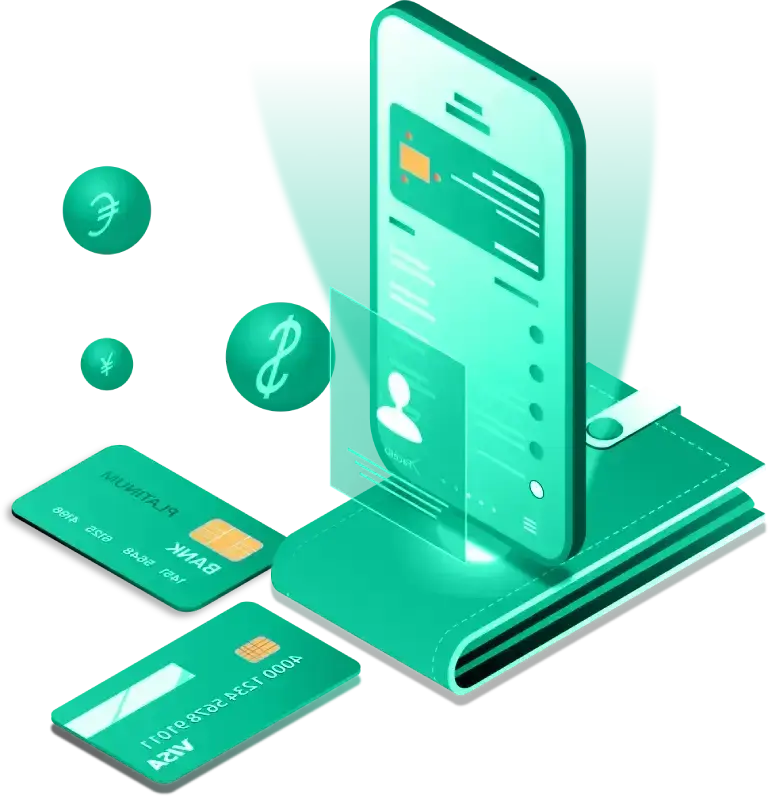
Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
